DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. DSL is enough new technology allows you to significantly expand the capacity of old copper telephone lines to connect telephone exchanges with individual subscribers. Be any subscriber who is greedy in present moment primary telephone call With the help of additional DSL technology, it is possible to significantly increase the speed of your connection, for example, to the Internet. Remember that to organize a DSL line, you need to use other telephone lines; This technology is good because it does not require laying additional telephone cables. As a result, you will give up full access to the Internet from the savings of normal telephone calls. Due to the diversity of DSL technologies, users can choose the most appropriate data transmission speed - from 32 Kbps to as low as 50 Mbps. These technologies also allow you to use the primary telephone line for such wide-area systems as video on demand or distance learning. Current technologies DSL brings the ability to organize high-speed Internet access for households and small businesses, converting high-speed telephone cables digital channels. Moreover, the speed of data transmission depends on the strength and length of the line that connects the customer and the provider. In this case, providers should give the customer the opportunity to choose the transmission speed that best suits his individual needs.
How does DSL work?
A telephone set installed in your home or office is connected to a telephone exchange via a twisted pair of copper wires. Traditional connection of purposes for emergency telephone calls with other telephony subscribers. In this case, analog signals are transmitted through the barrier. The telephone receives acoustic sounds (which are natural analog signals) and converts them into an electrical signal, the amplitude and frequency of which gradually changes. Since the entire telephone network is based on the transmission of analog signals, it is simplest, of course, to use this method itself for transmitting information between subscribers or the subscriber and the provider. You also need a modem that allows you to demodulate an analog signal and convert it into a sequence of zeros and ones. digital information, which is captured by the computer.
When transmitting analog signals, only a small part of the torsional transmission of a pair of copper telephone wires is lost; Thus, the maximum transmission speed that can be achieved using an additional modem is approximately 56 Kbps. DSL is a technology that involves the need to convert a signal from analogue form to digital form and vice versa. Digital data is sent to your computer as digital data, allowing you to use a wider variety of phone line frequencies. This makes it possible to simultaneously combine analog telephone calls and digital high-speed data transmission over the same lines, separating the spectra of their signals.
Brief description of different types of DSL technologies
DSL is a set of various technologies that allow you to organize a digital subscriber line. In order to understand these technologies and identify their areas practical zastosuvannya Let's understand how these technologies differ. First of all, first of all, we need to remember the relationship between the station on which the signal is transmitted and the data transmission speed, as well as the difference in the transmission speed of the “low” (from the point of view of the correspondent) and the “high” (in id koristuvacha to measure) the flow of data.
DSL combines the following technologies:
ADSL(Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line - asymmetric digital subscriber line)
This technology is asymmetrical, so the speed of data transfer from the control unit to the control unit is significant, but the lower speed of data transfer from the control device to the control unit. Such asymmetry, associated with the stage of a “permanently installed connection” (if the need to immediately dial phone number and check for connection installation), use ADSL technology, ideal for organizing access to the Internet, access to local networks (LAN), etc. When organizing such arrangements, the clerks remove much more information than they transmit. ADSL technology will ensure the speed of the “downstream” data flow from 1.5 Mbit/s to 8 Mbit/s and the speed of the “upstream” data flow from 640 Kbit/s to 1.5 Mbit/s. ADSL allows you to transfer data at a speed of 1.54 Mbit/s over a distance of up to 5.5 km using one pair of wires. Transmission speeds of about 6 - 8 Mbit/s can be achieved when transferring data to a station no more than 3.5 km long with wires with a diameter of 0.5 mm.
RADSL(Rate-Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line - digital subscriber line with speed adaptation)
RADSL technology ensures the same speed of data transmission as ADSL technology, but allows you to adapt the speed of transmission to the length and torque of a pair of wires. With the use of RADSL technology, connection on different telephone lines is possible There is a difference in liquidity data transfer. The data transmission speed can be selected when synchronizing the line, depending on the time of connection or the signal that comes from the station.
RADSL technology can ensure the flexibility of services provided by service providers to clients. This technology ensures automatic adjustment of the speed of data transmission along the line, which is based on a series of initial tests that allow us to determine the maximum possible speed of data transmission along a specific telephone line. Transmission speed at vicoristan ADSL technologies lie in the minds of many people, and first of all, there are too many subscriber lines and cable types that become stuck. As a rule, subscriber lines (that is, from the telephone exchange to the subscriber) can be divided over a wide range, and cables with different conductors are often twisted on the subscriber line. Izu. Therefore, the electrical characteristics of subscriber lines (and their extinguishing) can cause a significant difference. A factor such as changing the temperature of the cable can affect the permissible speed of data transmission, which can cause transmission along a single telephone line. Since RADSL allows you to automatically select the maximum possible speed of data transmission along each specific line, there is no need for labor-intensive manual adjustment ADSL lines.
In principle, RADSL means an xDSL modem that has the function of automatically adjusting the connection speed. Such a modem can automatically adjust the transmission speed up to electrical parameters lines. When the modem is connected to a long line, it automatically reduces the data transmission speed, ensuring that the connection is installed with the highest data transmission speed. Due to its adaptability, RADSL technology is susceptible to a large number of problems that can arise during DSL downtime.
The main advantages of RADSL are:
- Reduced labor costs for checking the subscriber line.
- Minimization of costs for services.
- One technology can be used in many areas.
- Simplification of the introduction of the system.
- Adaptation of transmission speed before changing the electrical characteristics of the subscriber line.
ADSL Lite
ADSL Lite is a low-speed (obviously, obviously) version of ADSL technology that will ensure the speed of the “downstream” data stream up to 1 Mbit/s and the speed of the “upstream” data stream up to 512 Kbit/s. ADSL Lite technology allows data to be transmitted over longer lines than ADSL, is easier to install and has less bandwidth, which ensures its benefits for the mass market.
IDSL(ISDN Digital Subscriber Line - IDSN digital subscriber line)
IDSL technology ensures duplex data transmission at speeds up to 144 Kbps. When administrated under ADSL, IDSL capabilities can only communicate with data transmission. Regardless of IDSL, ISDN, 2B1Q vicorist modulation, there are a number of features among them. When replaced with an ISDN line, the IDSL line is a line that is not switched, so as not to increase the burden on the switching service of the provider. Also, an IDSL line is “permanently extended” (as any line is organized using local DSL technology), whereas ISDN requires the establishment of a connection.
HDSL(High Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line)
HDSL technology transmits the organization of a symmetrical data transmission line, so that the speed of data transmission from the customer to the minimum and from the customer to the same level. With high speed transmission (1.544 Mbit/s over two pairs of wires and 2.048 Mbit/s over three pairs of wires), telecommunications companies are using HDSL technology as an alternative to T1/E1 lines. (T1 lines are installed in Western America and provide data transmission speeds of 1.544 Mbit/s, and E1 lines are installed in Europe and provide data transmission speeds of 2.048 Mbit/s .) If you want to get up, how the HDSL system transmits data (and this is close to 3.5 - 4.5 km), less, less often with the use of ADSL technology, for inexpensive, but effective, longer life of the HDSL line, telephone companies can install special repeaters. Victory for organizing an HDSL line of two or three torsion pairs telephone wires to use this system with ideal solutions for connecting PBX, Internet servers, local measures etc. HDSL II technology is a logical successor to the development of HDSL technology. This technology will provide characteristics similar to HDSL technology, but only requires one pair of wires.
SDSL(Single Line Digital Subscriber Line - single-line digital subscriber line)
Just like HDSL technology, SDSL technology will ensure symmetrical data transmission with speeds that correspond to the speeds of the T1/E1 line, in which case SDSL technology has two important dimensions. First of all, only one pair of wires is twisted, and in another way, the maximum transmission distance is 3 km. Between these stations, SDSL technology will ensure, for example, the operation of a video conferencing system if it is necessary to support new transmission streams directly. In short, SDSL technology is a predecessor of HDSL II technology.
VDSL(Very High Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line)
VDSL technology is the most advanced xDSL technology. It will ensure the speed of data transmission to the “downstream” stream in the range of 13 to 52 Mbit/s, and the speed of data transmission to the “upstream” stream in the range of 1.5 to 2.3 Mbit/s, and one twist of a pair of telephone wires. VDSL technology can be seen as a cost-effective alternative to laying fiber-optic cable at the end of the network. However, the maximum data transmission distance for this technology ranges from 300 meters to 1300 meters. That's it, because the subscriber's line does not have to be overcharged this value, or the fiber-optic cable must be brought closer to the seller (for example, there are establishments where there are a lot of potential sellers). VDSL technology can be used in the same way as ADSL; In addition, they can be used to transmit HDTV signals, video recording, etc.
SHDSL- Symmetric High Speed Digital Subscriber Line (symmetrical high-speed digital subscriber line)
SHDSL technology ensures symmetrical duplex transmission of information at speeds ranging from 192 Kb/s to 2.32 Mb/s over a dual-wire copper line. To increase the speed and range of the connection, two bets are traded.
Vikorist technology is a standard of 16-line linear encoding TC-PAM, which is spectrally incompatible with other data transmission technologies - long-distance telephone calls, ISDN, ADSL, VDSL and HDSL. The use of the TC-PAM coding system and the reduction of frequencies for downstream and upstream traffic allowed the most optimal use of all frequencies for transmitting traffic.
SHDSL technology effectively adapts transmission speed, which can vary from 8 Kb/s to 192 Kb/s to maximum value 2.32 Mb/s. For this purpose, following the G.hs.bis protocol, during the installation of modems at both ends of the line, the signal strength is tested and, as a result of the exchange of messages, the maximum transmission speed allowed for these signals is determined. With this maximum dozhina The connection (7.5 km at a speed of 192 Kb/s and more than 3 km at 2.32 Mb/s) is larger than other symmetric xDSL technologies that operate at the same transmission speeds. Suspension of echo suppression will ensure the surface of duplex connections at all values of fluidity.
In addition to ADSL, the SHDSL system will not require a POTS/ISDN splitter, which separates the information from analog phones, since the voice signal is segmented in the same way as the data signal is transmitted as an ATM packet and again Elections at the other end.
The main advantage of the SHDSL solution lies in the fact that SHDSL devices can work seamlessly with ADSL devices, just as the same xDSL technology is not compatible with the other xDSL.
To organize access to SHDSL technology, you need to see a direct line (physical line). Although SHDSL does not save the telephone channel, new Voice-over-DSL technology can be used to transmit digitized voice. Access bandwidth when connected via SHDSL is indicated technical characteristics, the length of a specific line connection that is connected to both the provider and the specific brand of SHDSL modem.
Advanced aspects of DSL technology
All DSL technologies (ISDN, HDSL, SDSL, ADSL, VDSL and S H DSL) are developed to ensure high-speed data transmission over telephone lines, which is primarily suitable for voice call the frequency spectrum is 300 Hz – 3.4 kHz. In the first place, it is necessary to ensure normal operation of DSL technology, which is used for high-speed data transmission of telephone lines that are responsible for removing the coil. Such coils were installed on several lines across the line and made it possible to move the telephone connection through long lines. The development of digital signal processing (DSP) technologies combined with new algorithms and coding technologies has made it possible to raise the information capacity of access to unprecedented heights. The width of the selected range of frequencies has increased by two orders of magnitude over the past decade: from approximately 100 kHz for commercial ISDN to less than 10 MHz for VDSL. Most DSL modem standards treat a DSL modem as a “pump for pumping fluids,” the main purpose of which is the smooth and reliable transmission of data between transceivers installed at both ends of the line, with a special connection We are looking for what includes song line parameters and noise models. The parameters of the line and the noise model are specially designed to represent the songs of the mind with which the modem has to “interact” with real measures access. Possible modifications, defined in the standards of DSL modems, lead to a stable signal-to-noise ratio, and an excellent speed of data transmission. To put it briefly, DSL modems are designed in such a way that they ensure the achievement of a Bit Reduction Ratio (BER) of no more than 107 according to similar testing standards. The access limit is the middle ground of external inflows, and most physical standards for DSL modems include all the steps below the basic benefits to ensure reliable data transfer and interoperability between the possession of various winegrowers.
Testing of subscriber lines is determined by the warehouse and topology (to ensure sufficient depth of technology advancement).
Crosstalk and surge capacity margin in the mode (allowance of interconnection with other DSL lines in one multi-pair cable).
Transmission speed (linear and less aggressive). Margin for resistance to pulse transients and noise through transient processes (acceptance of noise emissions, for example, when applying a call).
Reducing the spectral strength of transmission (to ensure spectral strength and minimize unnecessary disturbances in the radio frequency region of the spectrum).
Spend vibration (to ensure proper maintenance of the line and transmission of tension to the signal).
Linear interface symmetry (to avoid problems associated with electromagnetic interference).
Cycle synchronization and data scrambling (to avoid the cyclo-stationary effect, for example, the line-frequency spectrum).
Wake-up hour (to minimize delays, for example, during the hour of voice traffic transmission).
Three-dimensional displacement (to minimize data loss).
Launch protocols (confirmation of connection establishment).
Hot/cold start time intervals (the hour required to synchronize and achieve reliable transmission - to minimize the time the line is unavailable).
Linear encoding (to achieve effective bit/s up to Hz).
One-hour two-way transmission mode (sync, frequency, echo suppression).
Automatic correction of data transfers (for automatic correction of data transfer data physically, without the need to increase the intensity associated with the re-transmission of data, to high-level protocols).
Included operations and maintenance (for the transfer of information related to maintenance, such as maintenance).
ISDN-BA (DSL)
Short-term DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) was initially upgraded to ISDN-BA (access base level digital interconnection with service integration).
4-line PAM code (pulse amplitude modulation, direct, unmodulated transmission), produced by 2B1Q, manufactured by BT Laboratories. ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) has adapted this code for Europe and, as an alternative, developed the 4B3T (MMS43) line code, which is mainly used in Germany.
Most ISDN-BA modems use echo compensation technology, which allows for full-duplex transmission at a speed of 160 kbps over a single pair of telephone wires. ISDN-BA transceivers, which have echo cancellation technology, can handle a range of frequencies from approximately 10 kHz to 100 kHz, and the peak spectral density of DSL systems based on 2B1Q is in the region of 40 kHz with the first spectral zero at a frequency of 80 kHz. ISDN-BA systems are advantageous in that they can be hijacked on long telephone lines, and most subscriber lines allow hijacking of these systems. This technology has been under development for a significant amount of time, and over the past few years a significant reduction in the performance characteristics of transceivers has been achieved.
International ISDN-BA standards largely cover the transmission aspects of the physical level for the ISDN “U” interface or others wired interface. In Europe, there are edge services provided by the Telco company, which provide services via the S/T bus, which is based on the UNI (service provider edge interface) standard. Data transmission via a DSL line involves two channels “B” (information transmission channels) with a speed of 64 kbit/s on the skin, plus a channel “D” (service channel), which transmits a signal with a speed of 16 kbit/s and management and service information ,Sometimes can be used for packet data transfer. This will ensure the best possible access with a speed of 128 Kbit/s (plus transmission of service information – a total of 144 Kbit/s). An additional 16 Kbps service channel is provided for the EOC (Equipped Operational Channel), which is used for the exchange of information (for example, data line operation statistics) between LT (line terminations) and NT (line terminations). kinchennyam). Call for the use of an operational channel that is inaccessible to the terminal koristuvachevi.

Malyunok 1. Concept of the basic level of ISDN-BA (DSL).
Millions of ISDN-BA lines have been installed around the world. Demand for ISDN lines has increased significantly, as has the demand for high-speed Internet access.
The HDSL (High Speed Digital Subscriber Line) standard is similar to the ISDN-BA standard. The original HDSL concept was developed in Western America, and DSL distributors were trying to move forward clock frequency ISDN to see how far and how quickly high speed data transmission systems can operate. It is also important to note that DSP technology (digital signal processing technology) has developed rapidly at the same time. Doslednytska robot led to astonishing shock. It turns out that simple 4-line PAM modulation (pulse amplitude modulation) allows you to operate at speeds up to 800 Kbps with a very pleasant line usage (in the USA this zone is called Carrier Serving Area - zone operator service). There was a new technology for compensation of echo signals, which made it possible to organize two-way data transmission at 784 kbps speed over one pair of wires, which allows for easy access and the transfer and supply of fluidity, which is responsible for the supply of necessary servicing.
HDSL is a system of two-way symmetric data transmission (see Baby 2), which allows data transmission at speeds of 1.544 Mbit/s or 2.048 Mbit/s over multiple pairs of wires. Two linear codes are recommended: 2B1Q pulse-amplitude modulation and carrier-free amplitude-phase modulation (CAP). CAP modulation is used for transmission at a speed of 2.048 Mbps, while 2B1Q modulation is assigned to two different cycles.
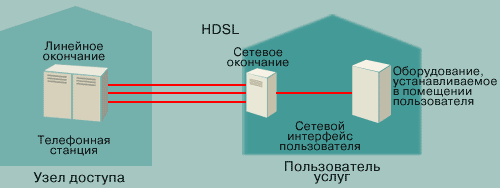
2. High speed digital subscriber line (HDSL) concept.
The 2B1Q standard for 2.048 Mbit/s will ensure two-way transmission over one pair of wires, as well as parallel transmission over two or three pairs of wires. This allows you to divide the data into multiple pairs and reduce the speed of transmission of symbols by increasing the limit of the line that can be transmitted. The CAP standard allows data to be transmitted over one or two pairs of wires, and the 2B1Q standard for speeds of 1544 Mbit/s only applies to two lines.
ADSL (asymmetrical digital subscriber line) technology was also introduced in Western America in the mid-1990s. It was split up to provide services such as those that require asymmetric data transmission, for example, video recording, if necessary. great flow data from the buyer, and at the same time, a much smaller amount of data is transferred to the buyer.
More high brightness transmission (the BER ratio is not less than 1 x 10-9), so there was a need for a technology for transmitting video streams with MPEG encoding, which is characterized by even high encoding and low overhead, if at all The eyes of the smile cast a significant influence on the brightness of the image. This required the use of new data transfer technologies and FEC (Full Encryption Correction), which were not completely different from ISDN-BA or HDSL. The price for this became an increase in the hour of recovery. Moreover, early ADSL systems had a low latency of 20 ms compared to ISDN-BA or HDSL, which did not exceed 1.25 ms.

3. Concept of asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL).
In addition to the fact that ADSL technology ensures extremely asymmetric data transmission, it also differs from ISDN-BA/HDSL in that it allows you to use the same pair of wires for traditional telephone calls. For this purpose, special devices are used for signals (splitters) (div. Figure 3).
ADSL uses FDD (Frequency Division for Full Duplex) technology, which allows you to see one set of frequencies for the upstream data stream (directly from the customer at the station), and another set of frequencies for the downstream data stream (from the station). ії in bіk koristuvacha) . This allows the range of frequencies to be expanded, which ranges up to approximately 1 MHz. Some ADSL variants use moon signal suppression technology, which allows for even better utilization of the available frequency spectrum, blocking part of the range occupied by the downstream data flow, transmitting data directly to the upstream one. The little one has 7 readings but uses the advanced FDD technology for upstream and downstream data flows and splitter.

Figure 4. ADSL application with frequency boosters and splitters.
Note: A high pass filter may be present at the input of the ADSL termination block.
Impedance weathering.
- Minimization of expenses.
- Podl spectrum of telephone communication and ADSL.
- saving the cost of telephone calls.
- Providing a stable transmission channel for ADSL.
The speeds of the outgoing and outgoing data flows vary and remain dependent on the subscriber's telephone line and noise level. Basically, ADSL communicates with transcodes at the far end of the line (FEXT), while ISDN-BA and HDSL communicate with transcodes at the near end of the line (NEXT). The very same exchanges that involve transcoding at the far end of the line allow transmission speeds for low data flows of 2 Mbit/s to be achieved on most subscriber telephone lines. The range of frequencies selected for the output data stream is significantly different from the technology, which means the speed of transmission of the output data stream reaches several hundred Kbit/s.
The ADSL transceiver can be used both for bit transmission and for ATM core transmission. mothers multi-service capabilities.
VDSL technology (Versus High Depth Digital Subscriber Line) is the result of a natural evolution of ADSL technology with higher data transmission speeds and a wider range of frequencies. This technology can be successfully introduced in the way of shortening the effective life of a subscriber line for the expansion of fiber optic lines and their deployment in This is a clear measure access. This architecture is shown as F T TC (Fibre to the Cabinet) and is shown in Figure 8, the VDSL concept is shown in Figure 5.

Malyunok 5. VDSL concept.
Symmetrical or double-wire DSL (SDSL) is symmetrical and is based on older HDSL technology, but also whole row more sophisticated, which allows flexible organization of data transmission over one pair of wires. SDSL technology can be used both in the business sector and in the private sector, which creates a very high potential value.
Varto respect that the people of today's distributors of high-tech commutation possession are looking at qiu technology as one of the ways to continue your lifelong possession this type. SDSL technology can be used in modern line cards that transmit 2 channels of switched traffic through a switching network. Any other high-speed access capabilities can be transferred from the switched network to the non-switched high-speed IP or ATM network. In addition, SDSL technology is compatible with digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) architecture and can be complemented by access technologies such as HDSL, ADSL and VDSL.
More details about these technologies, as well as about HDSL 2, SHDSL, RADSL, G. lite and ADSL 2, can be read in other articles on the site (XDSL technologies).
http://www.xdsl.ru/articles/

Description of ADSL technology
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) technology has been deployed to provide high speed (megabit) access to interactive video services (video, video games, etc.) and no less fast transmission them (access to the Internet, remote access to scrap and other measures).
First of all, ADSL is a technology that allows you to convert a couple of telephone wires into a high-speed data transmission path. An ADSL line connects two ADSL modems that connect to the end of a twisted pair telephone cable
In this case, three information channels are organized - a “downstream” data transmission stream, an “upstream” data transmission stream and a public telephone service (POTS) channel. The telephone communication channel is visible behind the help of filters, which guarantees that the robotic phone will respond to ADSL connection failures.
ADSL is an asymmetric technology - the speed of the “downstream” data flow (that is, the data that is transmitted from the bank terminal) is higher, the lower the speed of the “upstream” data flow (which is transmitted from the bank to the bank) zhi). It should be said right away that there is no reason to be concerned here. The speed of transmission from the computer ("more" direct data transmission) is, however, significant, lower than the analogue modem. In fact, the same thing is true, below ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network - Integrated digital measure zv'yazku).
To compress the large volume of information transmitted over twisted pairs of telephone wires, ADSL technology uses digital signal processing and specially created algorithms, advanced analog filters and analog-to-digital conversion. Long-distance telephone lines can attenuate the high-frequency signal that is transmitted (for example, at a frequency of 1 MHz, which is extreme Swissness ADSL transmission) by up to 90 dB. This allows analogue systems to be used by the ADSL modem to achieve the great benefits of a high dynamic range and low noise level. At first glance, the ADSL system is simple - it creates high-speed data transmission channels over a telephone cable. If you look at ADSL in detail, you can see that this system is up to date with current technology.
ADSL technology is a proprietary method of transferring a copper telephone line to a number of frequency bands (also called non-carriers). This allows you to simultaneously transmit a number of signals over one line. This very principle lies at the basis of the cable television network, when the operator uses a special converter that decodes the signal and allows you to watch a football match or a sizzling movie on the TV screen. With an ADSL connection, different parts of the data being transmitted can be transferred simultaneously. This process is known as frequency division multiplexing (FDM) (div. Figure 3). With FDM, one range is seen to carry the "upstream" data stream, and another range is seen to carry the "downstream" data stream. The range of the “downstream” flow is usually divided into one or a number of high-speed channels and one or a number of low-speed data transmission channels. The range of the "outgoing" stream is also divided into one or a number of low-speed data transmission channels. In addition, the technology of echo compensation (Echo Cancellation) may become stuck, when certain ranges of the “upstream” and “downstream” flows overlap (division 3) and are shared by the methods of local echo compensation.
With this method, ADSL can ensure, for example, one-hour high-speed data transmission, video signal and fax transmission. And all this without interrupting the original telephone connection, for which the telephone line itself is used. The technology transfers reserved frequency lines for voice calls (or POTS - Plain Old Telephone Service).
Advantages of ADSL over other technologies
- High fluidity data transfer (up to 8 Mbit/s), which significantly outperforms analog modems, ISDN, HDSL, SDSL.
- High stability of fluidity. When replacing cable modems, each subscriber receives his guaranteed bandwidth and does not share it with anyone.
- Nadiynyy link 24 years to get it.
- Low performance due to conversion of the original analog telephone line to ADSL.
- Lower (aligned with ISDN) connections up to the core of the line connection.
- The low service level of the line is equalized with the service level of the analog telephone line.
- Security of the data that is being transferred. The telephone line on which the ADSL modem operates is subscribed to by only one subscriber and is connected to another.
05/02/2005 | admin
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) includes high-speed data transmission technologies known as DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) technologies and can be used outside xDSL. Other DSL technologies include HDSL (High data rate Digital Subscriber Line), VDSL (Very high data rate Digital Subscriber Line) and others.
The original name of DSL technology was introduced in 1989, when the idea first emerged of analog-to-digital conversion at the subscriber end of the line, which would improve the technology of data transmission over a pair of copper telephone wires iv. ADSL technology has been developed to provide high-speed (one might say megabit) access to online video services (video on-demand, video games, etc.) and no less fast data transmission (access to the Internet, remote access to SCRAP and other measures).
What is ADSL? First of all, ADSL is a technology that allows you to convert a couple of telephone wires into a high-speed data transmission path. The ADSL line connects two ADSL modems, which are connected to the end of the twisted pair telephone cable (see Figure 1). In this case, three information channels are organized - a “downstream” data transmission stream, an “upstream” data transmission stream and a public telephone service (POTS) channel (div. Figure 2). The telephone dialing channel is visible behind additional filters, which guarantees that the robotic phone will respond in the event of an ADSL connection failure.
Fig.1. ADSL connection organization diagram

Fig.2. Distribution of frequencies in ADSL
ADSL is an asymmetric technology – the speed of the “downstream” data flow (the same data that is transmitted from the back end customer) is greater than the lower speed of the “upstream” data flow (the same data that is transferred from the backend customer). It should be said right away that there is no reason to be concerned here. The speed of transmission from the computer (“increased” direct transmission) is still significantly higher than when using an analog modem. In fact, the same thing is true: ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network).
To compress the large volume of information transmitted over twisted pairs of telephone wires, ADSL technology uses digital signal processing and specially created algorithms, advanced analog filters and analog-to-digital conversion. Long-distance telephone lines can attenuate the high-frequency signal being transmitted (for example, at 1 MHz, which has the highest transmission speed for ADSL) by up to 90 dB. This allows analogue systems to be used by the ADSL modem to achieve the great benefits of a high dynamic range and low noise level. At first glance, the ADSL system is simple - it creates high-speed data transmission channels over a telephone cable. If you go into detail about ADSL work, you can understand that given the system reach the reach of modern technology.
ADSL technology is a proprietary method of transferring a copper telephone line to a number of frequency bands (also called non-carriers). This allows you to simultaneously transmit a number of signals over one line. This very principle lies at the basis of the cable television network, where a special converter is installed that decodes the signal and allows you to watch a football match or a sizzling movie on the TV screen. With an ADSL connection, different parts of the data being transmitted can be transferred simultaneously. This process is known as frequency division multiplexing (FDM) (div. Figure 3). With FDM, one range is seen as transmitting the “upstream” data stream, and another range is for the “downstream” data stream. The range of the “downstream” flow is usually divided into one or a number of high-speed channels and one or a number of low-speed data transmission channels. The range of the "outgoing" stream is also divided into one or a number of low-speed data transmission channels. In addition, the technology of echo compensation (Echo Cancellation) may become stuck, when certain ranges of the “upstream” and “downstream” flows overlap (division 3) and are shared by the methods of local echo compensation.

Fig.3. Frequency amplification of communication line and echo compensation
With this technology, ADSL can ensure, for example, one-hour high-speed data transmission, video signal and fax transmission. And all this without interrupting the original telephone connection, for which the telephone line itself is used. The technology transfers a reserved line of frequencies for telephone calls (or POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service). It’s amazing how quickly the telephone calls changed not only to “plain” (Plain), but to “old” (Old); It just happened to be a good old telephone call. However, it is important to inform the distributors of new technologies that they still deprive telephone subscribers of a wide range of frequencies for live broadcasting. With this telephone Rozmova You can conduct one hour with high-speed transmission of data, rather than choosing one after the other. Moreover, as soon as you turn on the electricity, the original “good old” telephone connection will work as before, and with the call of an electrician you are not to blame for the problems you face every day. Providing such functionality was one of the parts of the original ADSL distribution plan. This capability alone gives ADSL systems an advantage over ISDN.
One of the main advantages of ADSL over other high-speed data transmission technologies is the reduction of high-torque pairs of copper wires in telephone cables. It is completely obvious that there are many more such pairs of darts (and this is an understatement), for example, cables laid specifically for cable modems. ADSL works, as one might say, “a barrier has been imposed.” Given how expensive it is, it takes a lot of time to upgrade the switching equipment (which is not necessary for ISDN) is not necessary.
ADSL is high speed data transmission technology, or how high speed? Considering that the letter “A” in the name ADSL stands for “asymmetric”, you can come to an unexpected conclusion that the transmission of data on one side is faster than on the other. Therefore, consider two types of data transfer: “downstream” flow (transferring data from the network to your computer) and “upstream” flow (transferring data from your computer to the network).
Factors that influence the speed of data transmission include the size of the subscriber line (such as the diameter of the wires, the presence of cable leads, etc.) and the length. The attenuation of the signal in the line increases with increasing line strength and increasing frequency of the signal, and changes with increasing dart diameter. The actual functional boundary of ADSL is a subscriber line with a length of 3.5 – 5.5 km with a wire thickness of 0.5 mm. At this time, ADSL will ensure the speed of the “downstream” data flow from 1.5 Mbit/s to 8 Mbit/s and the speed of the “upstream” data flow from 640 Kbit/s to 1 Mbit/s. The underlying trend in the development of this technology is expected to increase the speed of transmission, especially in the “downstream” direction.
In order to evaluate the speed of data transmission that is provided by ADSL technology, it is necessary to compare it with the speed that may be available to users who use other technologies. Analog modems allow data transmission at speeds of 14.4 to 56 kbps. ISDN provides data transmission speed of 64 Kbps per channel (if your system has access to up to two channels, it can reach 128 Kbps). Various DSL technologies provide the best possible data transmission speeds of 128 Kbps (IDSL), 768 Kbps (HDSL), downstream 1.5 – 8 Mbps and upstream 640 – 1000 Kbit/s ( ADSL), "downstream" flow 13 - 52 Mbit/s and "upstream" flow 1.5 - 2.3 Mbit/s (VDSL). Cable modems offer transmission speeds from 500 Kbps to 10 Mbps. (In this case, it is important to remember that the bandwidth of cable modems is divided among all the users who can access this line at the same time. Therefore, the number of users who are working at the same time significantly increases real fluidity data transmission from them.) Digital lines E1 and E3 have data transmission speeds of 2.048 Mbit/s and 34 Mbit/s.
With the use of ADSL technology, the transmission of the line, in addition to any terminal connection to the main circuit, must be carried out by that connection. Do you need an ADSL line? Virishuvat to you, but in order for you to accept correct decision Let's take a look at how ADSL works.
In advance, the speed of data transmission. The numbers are shown in two paragraphs above. Moreover, these numbers are the boundary. In the near future, the speed of the “downstream” stream will increase to 52 Mbit/s, and the “upstream” stream to 2 Mbit/s.
You no longer need to dial a number to connect to the Internet or LAN. ADSL creates a broadband transmission channel that is connected to the main telephone line. After installing ADSL modems, you will permanently remove connection installed. The high-speed transmission channel is always ready for operation - at any time, if you need it.
The transmission of the line must be ensured in its entirety. In addition to cable modems, which allow for limited transmission between network devices (which significantly affects the speed of data transmission), ADSL technology transmits short-circuit lines to only one network device.
ADSL technology allows the use of line resources at the same time. When making a phone call, Vikorist costs about one hundredth throughput capacity telephone lines. ADSL technology takes up only a fraction and uses up 99% of what is lost for high-speed data transmission. In this case, for different functions, use different frequencies. For telephone (voice) communication, the area of the low frequencies All line speeds are limited (up to approximately 4 kHz), and the network is configured for high-speed data transmission.
The rich functionality of this system is not the only argument for its benefit. In order to operate various functions, there are different frequency channels available for subscriber line bandwidth, ADSL allows you to simultaneously transfer data and communicate with your phone. You can make and receive phone calls, send and receive faxes, while surfing the Internet or receiving data from your corporate account. merezhi LOM. All on one phone line.
ADSL opens up new capabilities in areas where clear video signals are required in real time. These include, for example, the organization of video conferences, recording and recording of video. ADSL technology allows providers to provide their clients with services whose transmission speed is more than 100 times higher than that of the current market. Narazi An analog modem (56 Kbit/s) is more than 70 times faster than the data transmission speed of ISDN (128 Kbit/s).
ADSL technology allows telecommunications companies to provide a private communication channel to secure the exchange of information between the customer and the provider.
Don't forget about spending. ADSL technology is effective from an economical point of view, although it does not require the laying of special cables, but rather the use of dual-wire telephone lines. If you have a telephone at home or in the office, you do not need to lay additional wires for Wikoristannya ADSL. (I'd like to say this. The company that provides dial-up service is responsible for providing ADSL service.)
In order for the ADSL line to work, you don't need a lot of equipment. ADSL modems are installed at both ends of the line: one on the customer side (at home or in the office), and the other on the network side (Internet provider or telephone exchange). Moreover, it is not at all obligatory for customers to buy their own modem, rather than rent it from the provider. In addition, in order for the ADSL modem to work, you need a computer and an interface board, such as Ethernet 10baseT.

Fig.4. ADSL limit scheme
Today's data transmission technology, which was called ADSL, was able to reach a wider range. You should join the technology group under the name xDSL and use it everywhere to organize inexpensive and sufficient clear connection to global measure. The abbreviation stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. This additional technology will ensure high-speed Internet access, information transfer, and interactive services.
The essence of this method of data transmission, as well as all xDSL technologies, lies in the fact that the high-wire circuit carries the highest double-wire telephone lines. Previously telephone measures The transfer of information has already begun, and dial-up modems have finally stopped working. However, the connection speed, organized in this way, did not exceed 56 kbps. U vipadku z ADSL bandwidth Data transfer can reach high rates, on average up to 8 Mbit/s for download and up to 2 Mbit/s for upload (theoretically, it is possible to maintain 24 Mbit/s for the downstream and 3.5 Mbit/s for the upstream).
Such high results are achieved for rahunok povnogo vikoristannya line resources and the installation of two modems, one on the customer side, and the other on the telephone exchange. In addition, the telephone wire organizes three transmission streams: information: input and output streams, as well as a stream for voice communication. The work of the telephone connection does not lie at the same time, which makes it possible to make a telephone connection while connecting to the Internet.
Mutual switching off codes - the telephone channel is reliably stolen by the system that filters the vicor frequency range of 0.3-3.4 kHz, and the lower range of information transmission is 26 kHz. The high transmission speed is due to the use of special algorithms for compressing and transforming information. Converting a digital signal to analogue, transmitting it over a telephone cable and decrypting it is very easy. After this is removed, the digital signal goes to the provider, which will provide access to the Internet.
The main advantages of ADSL technology are:
- high speed of data exchange (the speed of switched connections exceeds at least 50 times);
- instantly ready to make a robotic connection, which does not require dialing a telephone number;
- outside of the line resources;
- instantly connect to the phone and connect to the limit;
- the ability to change the connection speed at different times of need without replacing the equipment;
- economically viable connection organization model
However, ADSL technology has its shortcomings:
- peredusim – length of the telephone line, cable support, signal attenuation, noise level;
- the maximum distance to the automatic telephone exchange is 6 km (in reality, the distance from the terminal to the port is 3.5 km to 5.5 km);
- the need to modernize lines (telephone distribution wire, which stagnates in most of the falls, it is necessary to replace it with a torsion pair);
- the need to add subscriber equipment (modem);
- the possibility of direct connection to a number of end subscribers via the ADSL infrastructure;
- The word “Asymmetric” in the name of the technology takes into account the importance of incoming traffic over outgoing traffic (comparing peer-to-peer networks, video communications and high-speed online TV).
Well, today ADSL is equally cheap and in a simple way organizing a mass connection to the Internet. It is clear that this technology is already quite outdated and secondary, and the infrastructure of networks organized behind fiber-optic cables is rapidly developing to replace it. Ethernet technologies and dartless merging WiMax (Wi-Fi).
Tim is not less, yet, regardless of all the shortcomings and boundaries, there are no real alternatives to xDSL in general and ADSL, for now. Obviously, in the mid-term perspective, fiber-optic connections will increasingly dominate the xDSL market in the access organization market, and in the long-term perspective, obviously, the future Internet will dartless lines. In the meantime, more than half of the Internet is connected to the Internet using additional xDSL technology and immediately create positions with these technologies, which are changing and evolving. Just like the application of such development – new technologies ADSL 2 and ADSL 2+…
