A computer, laptop, smartphone or tablet has two types of memory. The internal one is usually responsible for storing multimedia files and programs, but the operational one is working, in other words, temporary. Usually, modern devices have a sufficient supply of both memory, but it happens that the user needs its expansion. And if in the case of the internal one you can simply buy an external drive, then with the operational one this will not work.
What is it?
RAM is a temporary archive that stores the data of all programs for a certain period during their operation. After the device is turned off, the storage is cleared. Therefore, the PC always recommends the user to save all edited data, since after switching off the unsaved changes will disappear.
Usually, when it comes to "RAM", an archive is presented that stores all active processes and software. But sometimes this term is also called external drives such as disks or magnetic tape storage devices.
In general, all types of random access memory are volatile system elements. They store the machine code of the software, as well as input / output and intermediate materials on which the processor is working.
Historical background
Before we study the types and types of RAM, it is important to understand how it all started. The story begins already in the early 30s of the 19th century. Then he worked on an analytical engine. Those blocks that were supposed to store the interval costing results, he called "warehouses". All information about these cells was stored mechanically, in the form of the arrangement of shafts and gears among themselves.
When the first generation adding machine was created, its functionality was considered experimental. There is nothing to say about the "RAM" at all. There were several alternatives to it, and they were based on physical principles. Have been associated with acoustic delay lines, cathode ray tubes, etc.
Then the RAM could have an absolutely unpredictable appearance. Most often they were magnetic drums or shafts.
With the release of the second generation of computers, it was necessary to think about effective RAM. It was then that magnetic cores with memory appeared. The third generation took a leap forward and began to use microcircuits on which there were electronic components of a computer. Then the types of random access memory had already begun to appear. The dynamic was maintained thanks to the charge of the capacitor, and the static was maintained with the help of triggers.
The current state of affairs
Over time, the technological process has led to the latest type of RAM. "Operative" still depends on the supply of energy. In the event of a loss of power, it immediately loses all unsaved data. Nowadays, there are the main types of random access memory. There are two of them, as before: static and dynamic. The first works thanks to the trigger, the second - the capacitor. 
Both have become more efficient. Outwardly, they look like a module with semiconductors, which is organized like a device with free access. Dynamic memory is an order of magnitude cheaper. Next, we'll take a closer look at each of them.
Dynamics at work
Random access memory has different types. Among the main ones are dynamic, or DRAM. This is the most common form in computers. Due to the fact that it is more economical. To store the discharge, a special circuit was developed, which consists of two parts: a capacitor and a transistor.
This structure is much cheaper and also economical. This is because more capacitors and transistors can fit on one crystal than in another version of the module.
The main disadvantage of such a "RAM" is its speed. It works slowly, since it takes additional time to change the status of the capacitor: discharging and charging. This process takes ten times more than the static version. Also, this form has another drawback, in which the capacitors are discharged over a period of time. Moreover, this may be due to electrical capacity and greater current leakage.
It is because of the last drawback that this species received such a name: the charge decreases with time, which means that dynamics is observed. However, so that all information is not lost, the capacitor can regenerate over time, thus extending its life. To start the recovery, you must enable the readout sequence. It touches all lines of the memory matrix. This event regulates the processor or memory controller.
Statics
This is a kind of random access memory made from transistors. SRAM does not require restoration, which is why it got its name. The main advantage of this memory is its high speed. This is due to the fact that the mechanism for attaching triggers and logic gates is simple, so it does not take much time to switch the first ones. 
But you have to put up with the high cost and waste. The fact is that the transistors that are in the flip-flops are much more expensive than in the first type of memory. They do not affect their high cost and group manufacturing methods. Also, transistors take up too much space on a single die.
Static RAM is almost never used in modern PCs. Usually it is placed for the sake of organizing ultra-fast RAM, which can harm system performance, and it is critical.
Appearances are deceptive
To outwardly determine the types of computer RAM, you need to understand them very well. An ordinary user cannot do this. Unless we are talking about modules for a PC and laptop.
Nevertheless, nowadays several types of random access memory can be classified. Some of them are used today, some have long ceased to appear on the market, but they can still be found in computers of the old generation. Moreover, many of the previous models turned out to be much more tenacious than the newfangled options.
FPM
This is dynamic random access memory. The principle of its operation is simple: it receives data faster from the page that was used in the last cycle. This technology is named Fast Page Mode. Nowadays it is very rare to find such a "operative", since it served in the mid-90s of the last century. Then her companions were the 486 processors and the new Pentium. 
EDO
This is another random access memory, the types of which are not widely known. Previously worked as early as 1995 and was specially prepared for the first Pentium processor. It has become an improved version of the previous one. She worked on two actions at once: she selected the next block while sending the previous one to the processor.
SDRAM
A very smart version of RAM. It is so fast that it can easily interact with the frequency of the processor. The principle is more complicated: the microcircuit has two parts. In the process of active work, in the first of them there is a reference to the bit, and in the other, preparation of this action. This module became popular in 1996. Then it was actively used in cooperation with Intel. It was fruitful enough that SDRAM was popular until 2001.
This RAM has overtaken the previous types with interest. It became three times faster than FPM and twice as fast as EDO. It worked at 133 MHz. 
DDR
This is an improved version of the previous one. It appeared just in 2001. The main change affected not the clock frequency, but the work itself. Now, in one clock cycle, data was transmitted two times.
DDR2
It is clear that this version is a continuation of the previous one. It appeared in 2003, but the chipsets for it were made only the next year. Just like the previous "congener" DDR2, it can transfer data twice per clock. The main difference between the two modules is the modified one, which was obtained due to structural improvements. This version did not live long as it had some drawbacks. Due to the increased frequency, it slowed down noticeably in the process of working with memory. ![]()
DDR3
Another equally well-known RAM is DDR3. The types of these "RAM" belong to the SDRAM series. She replaced the previous generation. Is used for computing devicesand also for video memory.
This version of the module has become more gentle: it saves up to 40% of energy. The power supply was reduced by using a 90nm technical processor. In this case, a microcircuit and double-gate transistors were made, which are precisely responsible for the leakage of currents.
The trouble was that this time the module turned out to be modified. Its key is now in a different place, so it is impossible to install this RAM in place of DDR2. Nevertheless, this was done for a reason. The electricity parameters do not match for these modules, therefore, to avoid erroneous installations, the location of the key was changed.
DDR4
New evolutionary random access memory. The types of SDRAM have come to their logical conclusion. The new module was released to the masses in 2014. It improved the frequency response and reduced the supply voltage. The main difference from the previous generation: the doubled number of banks (16 units). 
The bandwidth is now also much better and can theoretically reach as much as 25 GB / s. Developed and new technologywhich increases the reliability of all processes. This RAM has its own processor - Intel Haswell-E / Haswell-EP.
RAMBUS
This is a separate random access memory, types, the characteristics of which are quite high. It was developed in 1996. Intel decided to tackle it. "Operative" turned out to be an order of magnitude better than its "colleagues". Well-known concerns received a license for it. Later, several motherboards were created for it. She showed excellent results on them.
It so happened that before its release, Intel discovered an error, because of which it lost about $ 100 million. Now this module is rarely used. But it is still found in PlayStation 2 and PlayStation 3.
Laptops
The difference between RAM for laptops and PCs is noticeable only in size and names. Therefore, there is no point in repeating all of the above. To select a module for this device, you must also study all existing species RAM for a laptop, determine its compatibility with motherboard and deal with the price category.
The first "RAM" for the laptop was released in 2002. It was the SO DIMM SDRAM model. Now it is no longer possible to find it anywhere. It worked at 100 MHz and 133 MHz. SO DIMM DDR appeared a little later - in 2005. It has become an order of magnitude more powerful. Received 266, 333 and 400 MHz frequencies. The location of the key has changed significantly compared to the previous model. SO DIMM DDR2, relative to its “colleague” from the previous generation, also became more powerful: maximum frequencies reached 800 MHz. The key shifted again, but by 1 mm, compared to DDR, which led to confusion with compatibility.
SO DIMM DDR3 entered the market in 2009. The location of the key was radically different from the previous model, so inexperienced users now could not be mistaken. The maximum frequencies of this module have reached 1600 MHz.
Laptop models have changed, modified, and the RAM for them has also been transformed. The next module was Micro DIMM DDR2. Its volume was 1 GB, which was quite a lot for the user. 
Now the situation with RAM for a laptop is twofold. The fact is that many models have an integrated system, and it is not possible to replace the "RAM". Therefore, the demand for modules for laptops is now very small. Those who still need to increase the volume of temporary storage spend a lot of time to find a good option.
Now, in order for a computer to cope with surfing the Internet and office programs, 1 GB of "RAM" will be enough. But gamers should look at the more powerful options. For example, Kingston SO-DIMM DDR3 4Gb PC10660. This operational costs almost 2 thousand rubles. Its volume, as the name implies, is 4 gigabytes. The type is DDR3, and the clock speed is 1333 MHz.
Other companies that produce quality modules include Samsung, Corsair, Hynix, Transcend. For desktop PC owners, there are some very powerful options that PC gamers will especially love - the Kingston HyperX FURY Red Series. The set of "RAM" includes two 4 GB modules. The type is DDR3, and the clock speed is 1866 MHz. The price of such RAM is 3500 rubles.
Random access memory is one of the main components of a computer; without it, the operation of the system is impossible. The amount and characteristics of the RAM installed in the system directly affect the speed of the computer. Let's find out at a simple consumer level what it is and why it is needed in a computer at all.
As it is already clear from the name, computer RAM or RAM (random access memory) in the computer jargon "RAM", as well as simply "memory" is used for operational (temporary) storage of data necessary for work. However, such an explanation is not completely clear what temporary means and why they should be stored in the RAM when there is hDD.
Here we come to the fundamental difference in the structure and purpose of these two computer subsystems. In the article dedicated to the hard drive, we have already touched on this issue and for a better understanding of the issue, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with it. Here we will take a closer look at the issue from the side of the computer's RAM. Since the material is intended for novice computer users and people who want to understand in more detail in its device, we will not delve into standards, technical implementations different types RAM and other complex technical moments, interesting only to engineers, but consider this issue from the standpoint of an ordinary person.
The easiest way to answer the question is what does it mean to temporarily store data. The design of RAM is made in such a way that data is stored in it only as long as voltage is applied to it, therefore it is volatile memory, unlike hard disk... Turning off the computer, rebooting clear the RAM and all data in it at this moment is deleted. Even a short interruption in the voltage supply to the memory strips can reset them or cause damage to a separate piece of information. In other words, the computer's RAM stores the data loaded into it within a maximum of one computer session.
The second part of the question, why is it needed at all, is a little more difficult to understand. Here it is already necessary at least in general terms to imagine the device of a computer, so we advise you to read this article, as well as the interaction of various components, which is described among themselves in the material on the computer motherboard.
So, RAM serves as a buffer between the central processor and the hard drive. A hard disk is non-volatile and stores all information in a computer, but the price is its slow speed. If the processor took data directly from the computer's hard drive, it would act like a turtle. The solution to this problem is the use of an additional buffer between them in the form of random access memory.
Memory is volatile and requires constant power supply for its work, but it is much faster. When the processor needs some data, this data is read from the hard drive and loaded into the RAM, and all further operations with them occur in it. Upon completion of work with them, if the results need to be saved, then they are sent back to the hard disk for writing to it, and they are deleted from the RAM to make room for other data. If the results do not need to be saved, the computer's RAM is simply cleared.
This is how their interaction looks in a highly simplified form. Besides central processing unit information from RAM may be required by other components, for example, a video card. Naturally, a lot of data is stored in memory at the same time, since all programs that you run or files you open are loaded into it. The files of the browser through which you are now looking at this site, as well as the Internet page itself, are located in RAM.
It is worth noting that the data from the hard disk is copied into the RAM, so until the changes made with them are saved back to the disk, they will remain there. old version... For this reason, having opened, for example, a Word file and making some changes to it in the editor, you need to save at the end, while the file is loaded back to the hard disk and overwrites the one stored there.
Various components of the computer do not interact directly with each other, but through various interfaces, so the system bus is used to exchange information between the processor and RAM.
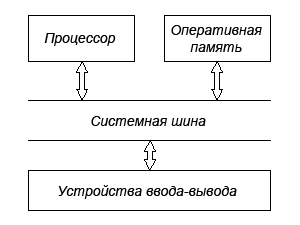
The performance of the entire computer depends on the speed of all its components and the slowest of them will be a bottleneck that slows down the operation of the entire system. The advent of RAM significantly increased the speed of work, but did not solve all the problems. First, the RAM speed is not ideal, and secondly, the connecting interfaces also have bandwidth limitations.
Further development of technology has led to the fact that in devices requiring high data processing speed they began to build their own memory, this eliminates the cost of transferring data back and forth, and usually in such cases a faster memory is used than that used in RAM. An example would be a video adapter, built-in CPU cache, and so on. Even many hard drives now have their own internal high-speed buffer, allowing faster read / write operations. The answer to the question why this high-speed memory is not used now as operational memory is very simple, some technical difficulties, but the main thing is its high cost.
As applied to typical computers, RAM comes in the form of modules that are installed in a special slot on the motherboard. The dimensions and shape depend on the applicable standard, but in general it looks something like the figure.

However, memory modules with high speed characteristics and focused on a high-performance computer system or overclocking may differ significantly in appearance from their ordinary counterparts. Manufacturers can add various additional elements, such as radiators, to improve cooling and stability at high frequencies. An example is this OCZ module with a heatpipe heatsink installed.

Types of RAM
On this moment time, there are two types of memory possible for use as random access memory in a computer. Both are random access semiconductor memory. In other words, memory that allows you to access any of its elements (cells) by its address.
Static memory
SRAM (Static random access memory) is made on the basis of semiconductor triggers and has a very high speed work. There are two main disadvantages: high cost and takes up a lot of space. Now it is used mainly for small-capacity cache in microprocessors or in specialized devices, where these disadvantages are not critical. Therefore, we will not consider it further.
Dynamic memory
DRAM (Dynamic random access memory) is the most widely used memory in computers. It is built on the basis of capacitors, has a high recording density and a relatively low cost. The disadvantages arise from the peculiarities of its design, namely, the use of small capacitors leads to a rapid self-discharge of the latter, so their charge has to be periodically replenished. This process is called memory regeneration, hence the name dynamic memory. Regeneration noticeably slows down the speed of its operation, therefore, various intelligent schemes are used to reduce time delays.
The development of technology is progressing at a rapid pace and the improvement of memory is no exception. Computer random access memory currently in use dates back to the development of DDR SDRAM memory. It doubled the operating speed in comparison with previous designs by performing two operations per clock cycle (on the edge and on the cutoff of the signal), hence the name DDR (Double Data Rate). Therefore, the effective transmission frequency is twice the clock frequency. Now it can be found almost only in old equipment, but DDR2 SDRAM was created on its basis.
In DDR2 SDRAM, the bus frequency was doubled, but the latencies increased slightly. Due to the use of a new housing and 240 pins per module, it is not backward compatible with DDR SDRAM and has an effective frequency of 400 to 1200 MHz.
The most common memory nowadays is the third generation DDR3 SDRAM. Due to technological solutions and a decrease in the supply voltage, it was possible to reduce power consumption and raise the effective frequency from 800 to 2400 MHz. Despite the same housing and 240 pins, DDR2 and DDR3 memory modules are not electrically compatible with each other. To prevent accidental installation, the key (notch in the board) is located in a different location.
DDR4 is a promising development that will soon replace DDR3 and will have lower power consumption and higher frequencies, up to 4266 MHz.
Along with the frequency of work, timings have a great influence on the final speed of work. Timings are the time delays between a command and its execution. They are necessary so that the memory can "prepare" for its execution, otherwise some of the data may be corrupted. Accordingly, the lower the timings (memory latency), the better and therefore the faster the memory, all other things being equal.
There are many different timings, but usually there are four main ones:
- CL (CAS Latency) - the delay between the command to read and the beginning of data receipt
- T RCD (Row Address to Column Address Delay) - the delay between sending the command to activate the line and the command to read or write data
- T RP (Row Precharge Time) - the delay between the command to close a line and open the next
- T RAS (Row Active Time) - the time between the activation of the line and its closing
They are usually specified as a string of digits separated by a hyphen, for example 2-2-3-6, if only one digit is specified, then the CAS Latency parameter is implied. This allows you to compare the speed of operation of different modules and explains the difference in the cost of seemingly identical strips.
By the way, usually the larger the module size, the higher the timings, so taking two 2 GB slats may be more profitable than one 4 GB. In addition, the use of several identical memory strips activates the multichannel operation mode, which provides an additional increase in performance. For the sake of fairness, it should be noted that at present the impact of timings on performance has slightly decreased due to the widespread increase in the cache size based on high-speed static memory integrated into modern processors.
How much RAM to use
The amount of memory that can be installed in a computer depends on the motherboard. The amount of memory is limited both physically by the number of slots for its installation, and to a greater extent by the software limitations of a particular motherboard or installed computer operating system.
In general, 2 GB is enough to browse the Internet and work in office programs, if you play modern games or are going to actively edit photos, videos or use other programs that require memory space, then the volume installed memory should be upgraded to at least 4 GB.
Please note that Windows operating systems are currently available in two flavors: 32-bit (x32) and 64-bit (x64). The maximum volume available to the operating system in 32-bit versions, depending on various combinations of components, is approximately 2.8 to 3.2 GB, that is, even if you install 4 GB in your computer, the system will see a maximum of 3.2 GB. The reason for this limitation appeared at the dawn of the emergence of operating systems, when no one, even in the brightest dreams, would have thought about such amounts of memory. There are ways to allow a 32-bit system to work with 4 GB of memory, but these are all "crutches" and do not work on all configurations.
Also, Windows 7 Starter has only a 32-bit version and is limited to a maximum of 2 GB of RAM.
64-bit versions of the operating system do not experience such problems, for example, Windows 7 Home Basic supports up to 8 GB, and Home Extended up to 16 GB. If suddenly this is not enough for you, you are welcome to use the Professional, Corporate or Maximum versions, where you can install up to 192 GB of memory, the main motherboard, where you put all this wealth, do not forget to find and so that you still have enough money.
How to find out what kind of RAM is in the computer
There are two ways to determine the type and characteristics of memory installed in your computer. You can see this data on the sticker attached to the module itself, although you will probably have to remove it from the slot, otherwise you will hardly see anything. If the sticker with information is missing or unreadable, then the type of DDR memory can be determined by the number of contacts and the location of the key (notch) on the strip. Use the figure below to do this.

Another way to find out comprehensive information about the characteristics and operating mode of RAM is to use some program that displays information about the system. We recommend using free program CPU-Z showing, including characteristics and mode of memory operation.

The Memory tab displays the type of RAM installed in the computer, its size, operating mode and used timings. The SPD tab shows all the characteristics of a particular memory module installed in the selected slot.
What is SPD
Every modern memory module contains a special chip called an SPD. This abbreviation stands for Serial Presence Detect and in this microcircuit the manufacturer writes all information about this module, including the volume, marking, manufacturer, serial number, recommended delays and some other information. During bootstrap This information is read by the BIOS from the SPD chip and, in accordance with the specified settings, the memory operating mode is set.
The last thing a novice user should know is that there is both buffered (registered) and ECC memory. RAM with ECC (Error Checking and Correction) support allows you to correct some errors that occur during data transfer. Buffered memory modules contain a built-in buffer of a specific size to increase reliability and reduce the load on the memory controller. Both of these types of memory are intended for use in workstations and servers and in personal computers are not used.
There are a lot of types of random access memory on the market now. It is difficult for a non-versed user to do right choice... And having come to the store, it happens like this: the sales assistant, taking advantage of the buyer's ignorance, does not always sell him what he needs. Therefore, I decided to write a detailed article about this so that any person, after reading it, chooses a RAM module with confidence. Going to the store for a purchase, you just need to decide for which PC the memory is purchased (budget, universal and gaming), what volume, frequency and company. In this article, I will consider RAM from "A" to "Z".
Note! RAM is used to temporarily store data and instructions that are needed for the operating system. Excessive RAM does not always increase PC performance.
RAM form factor
There are three types of random access memory. This is worth paying special attention to. There is nothing difficult here.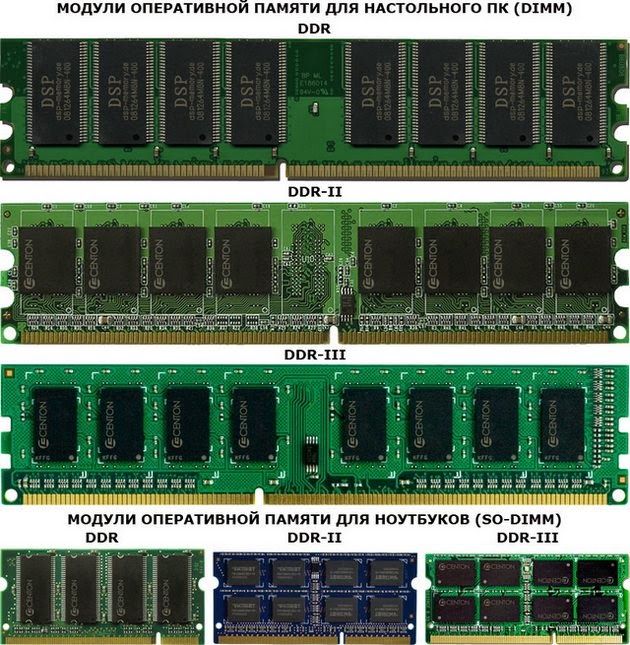
DIMM - this type of random access memory is used in personal computers.
SO-DIMM - this type is intended for and laptops. In terms of their characteristics, they are the same as DIMMs, only smaller in size.
FB-DIMM Is a special type of random access memory with improved reliability and buffering support. This memory is used in servers.
When buying, you need to know what kind of RAM your motherboard supports. At the time of this writing, there are four types on the market. DDR and DDR2 are already outdated, but you can buy them from stock at a price higher than DDR3 (since they were out of production). But DDR3 memory modules now dominate the market. DDR4 memory appeared this year.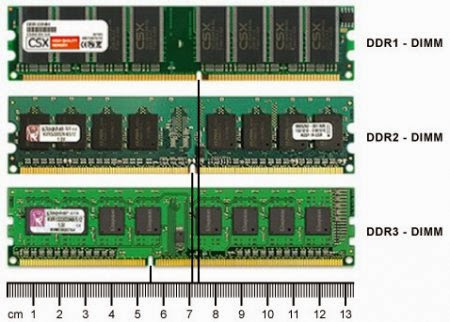
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that the types of RAM are incompatible with each other.
RAM clock speed
I don't think it's worth explaining here: the more the better. True, there are pitfalls. First of all, you need to look at what frequency the motherboard supports. For example, you have a 2400 MHz RAM stick, and the motherboard supports 1800 MHz. So, the speed of work will not increase. And by such actions you will lose 600 MHz and the difference in money.
Now the most popular are DDR3 memory modules with a frequency of 1333 MHz and 1600 MHz. But soon they will be replaced by DDR4 with a frequency from 2133 to 4266 MHz.
RAM size
At the beginning of the development of RAM, their volume was measured in kilobytes and megabytes. Now, of course, everything has changed dramatically. The more memory, the more information fits into the chip. How to choose the right volume?2 GB - perfect for budget PC options (Internet surfing, watching movies, photos, etc.)
4 GB - well suited for demanding programs and games at medium quality settings
8 GB - this volume is enough for modern head games
16 GB - all programs and games will fly
32 GB - a waste of money, better to buy
or a video card (will significantly increase the work of your PC)
On a note! 32-bit operating system Windows does not see RAM more than 3 GB. Even if you go broke and install a 32GB memory module, Windows will only recognize and use 3GB. Don't trust anyone about fixing this problem with software. Here you need to install a 64-bit version of Windows.
Timing and latency
Few people know about this parameter, and they do not pay attention to it.Latency (timing) is the signal latency when the processor is working with memory. Timing ranges from 2 to 13. The lower the number, the better. But with an increase in the frequency of RAM, the timing increases. So you need to take into account the ratio of these parameters.

Timing is written as three numbers 2-2-2, 3-3-3, etc. Each number is a parameter. Let's start in order.
CAS Latency - working cycle time
RAS to CAS Delay - access time
RAS Precharge Time - pre-charge time
Cooling system
We all know that the candy bar, PC and laptop get very hot during operation. Imagine, RAM can get warm too. In this regard, manufacturers began to equip memory modules with cooling shrouds. Expensive models have their own own system cooling.

Here I want to advise you to buy RAM with at least minimal cooling.
Operating memory modes
If your motherboard allows multiple modes, then rejoice! RAM can work in 1,2,3,4 channel mode. In two-channel mode, the system works 2 times faster, etc.
Let's take a closer look at all types of modes:
Single chanell Mode - this is a single-channel or asymmetric mode, which is activated when the system has 1 memory module or all modules differ in frequency, memory size or manufacturer. Whatever RAM is connected, everyone will work at the slowest.
Dual Mode - dual-channel mode works when identical RAM modules are installed. This doubles the speed. It is important to know here that the modules work in pairs 1 with 3, and 2 with 4.
Triple Mode - three-channel mode working on the principle of two-channel. But in practice it is not always more productive than a two-channel one.
Flex Mode - this is a flexible (mixed) mode, when performance increases regardless of the type of RAM. The main thing is that they have the same frequency. In my opinion, this mode is the best.

The most common is the two-channel mode. For multi-channel mode, you need to buy special memory modules. They are called Kit-memory. Sold in a set in which the RAM is the same.
RAM marking
There is a lot to tell by the look and markings on the memory module. As an example, I will cite the RAM from Kingston.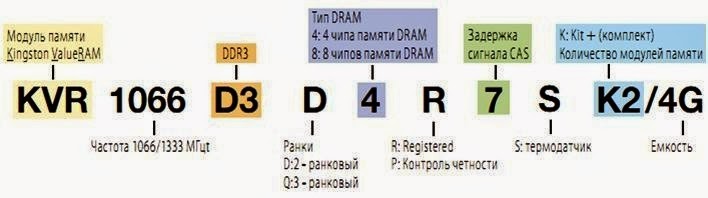
1. KVR - manufacturer
2. 1066/1333
- operating frequency
3. D3 - type of RAM (DDR3)
4. D-rank - this means that the memory has a dual channel mode
5. 4
- means that the RAM has 4 memory chips
6. 7
- signal delay is 7
7. S - there is a thermal sensor on the module
8. K2 - consists of a Kit
9. 4G - Kit memory capacity is 4 GB
Conclusion
I hope I wrote the article clearly. I can't say anything about manufacturers, because it doesn't matter which manufacturer, since RAM modules rarely break. And the price will primarily depend on the characteristics. Bottom line, the main thing is to know what characteristics of RAM your motherboard supports.There are several common types of memory modules used in modern computers and computers released a few years ago, but still working in homes and offices.
For many users, distinguish them both by appearanceand performance is a big problem.
In this article, we will look at the main features of different memory modules.
FPM
FPM (Fast Page Mode) is a type of dynamic memory.
Its name corresponds to the principle of operation, since the module allows faster access to the data that is on the same page as the data transferred during the previous cycle.
These modules were used on most 486-based computers and early Pentium-based systems around 1995.
EDO
EDO (Extended Data Out) modules appeared in 1995 as a new type of memory for computers with Pentium processors.
This is a modified version of FPM.
Unlike its predecessors, EDO starts fetching the next block of memory at the same time it sends the previous block to the CPU.
SDRAM
SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) is a type of random access memory that works so fast that it can be synchronized with the frequency of the processor, excluding standby modes.
The microcircuits are divided into two blocks of cells so that when a bit is accessed in one block, there is preparation for accessing a bit in another block.
If the access time to the first piece of information was 60 ns, all subsequent intervals were reduced to 10 ns.
Beginning in 1996, most Intel chipsets began to support this kind of memory modules, making it very popular until 2001.
SDRAM can run at 133 MHz, which is almost three times faster than FPM and twice as fast as EDO.
Most computers with Pentium and Celeron processors released in 1999 used this type of memory.

DDR
DDR (Double Data Rate) has become the development of SDRAM.
This type of memory modules first appeared on the market in 2001.
The main difference between DDR and SDRAM is that instead of doubling the clock frequency to speed up operation, these modules transfer data twice in one clock cycle.
Now it is the main memory standard, but it is already beginning to give way to DDR2.

DDR2
DDR2 (Double Data Rate 2) is a newer version of DDR that should theoretically be twice as fast.
DDR2 memory first appeared in 2003, and chipsets supporting it in mid-2004.
This memory, like DDR, transfers two sets of data per clock.
The main difference between DDR2 and DDR is the ability to operate at a significantly higher clock speed due to design improvements.
But a modified scheme of work, allowing you to achieve high clock frequencies, at the same time increases the latency when working with memory.

DDR3
DDR3 SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory, 3rd generation) is a type of random access memory used in computing as RAM and video memory.
Replaced DDR2 SDRAM memory.
DDR3 has a 40% lower power consumption compared to DDR2 modules, which is due to the lower (1.5 V, compared to 1.8 V for DDR2 and 2.5 V for DDR) voltage supply of memory cells.
Reducing the supply voltage is achieved through the use of a 90-nm (initially, then 65-, 50-, 40-nm) technical process in the production of microcircuits and the use of Dual-gate transistors (which helps to reduce leakage currents).
DIMMs with DDR3 memory are mechanically incompatible with the same DDR2 memory modules (the key is located in a different place), therefore DDR2 cannot be installed in slots for DDR3 (this is done in order to prevent incorrect installation of some modules instead of others - these memory types do not match by electrical parameters).

RAMBUS (RIMM)
RAMBUS (RIMM) is a type of memory that appeared on the market in 1999.
It is based on traditional DRAM but with a completely redesigned architecture.
The RAMBUS design makes memory access more "intelligent", allowing for preliminary access to data, slightly offloading the CPU.
The main idea used in these memory modules is to receive data in small packets but at a very high clock speed.
For example, SDRAM can transfer 64 bits of information at 100 MHz, and RAMBUS - 16 bits at 800 MHz.
These modules were not successful as Intel had many problems implementing them.
RDRAM modules have appeared in the Sony Playstation 2 and Nintendo 64 game consoles.


Translation: Vladimir Volodin
Debuts Intel Optane 900p SSD Line with 3D XPoint
Intel has officially unveiled the first solid state drives for PCs and workstations based on the 3D XPoint perspective memory.
The devices are part of the Optane 900p line, available in versions of 280 and 480 GB, and their main advantages over competitors' solutions, as in the case of server counterparts, are high performance when working with small files along with a large recording resource.
Intel Optane 900p drives are available in both low-profile PCI-E expansion cards and 2.5-inch U.2 devices (280GB models only).
In both cases, four lines of the PCI Express 3.0 interface act as the information transmission channel.
The maximum sequential read and write speeds are 2500 and 2000 MB / s, respectively, and the performance when working with random 4K blocks reaches 550 thousand IOPS when reading and 500 thousand operations when writing.
One of the advantages of the presented NVMe drives is their resource.
The TBW parameter (total number of bytes written) for the 480GB model is 8760 TB, while for the 280 GB model it is 5110 TB.
Thus, these drives can be guaranteed to be rewritten over 18 thousand times.
As for the recommended cost, the Intel Optane 900p drive with a volume of 480 GB will cost at least $ 600, and the 280 GB model was estimated by the chip maker at $ 390.
All devices are covered by a five-year manufacturer's warranty.
New sets geForce drivers 388.10 and Radeon Crimson ReLive 17.10.3
The release of Wolfenstein: The New Colossus has pushed AMD and Nvidia to release fresh driver packages to address instability issues in the new shooter.
Both releases are beta-versions and do not include new game optimizations.
Radeon Software Crimson ReLive Edition 17.10.3 Driver Pack fixes freezes and crashes in Wolfenstein: The New Colossus and Destiny 2 on Radeon RX Vega series graphics adapters.
Game optimizations for these projects are included in the "red" set of drivers, starting with previous version (17.10.2).
Meanwhile, Nvidia, in order not to make gamers wait for the release of the Game Ready driver, optimized specifically for the new shooter from MachineGames, has released a small patch in the form of the GeForce 388.10 Hotfix.
The key task of the new release was to ensure stable operation of Wolfenstein: The New Colossus on Kepler generation video cards.
A full Game Ready driver is slated for release next week.
New malware for stealing money from ATMs
Kaspersky Lab has discovered a new malwareallowing attackers to steal money from ATMs.
The malware is reportedly named Cutlet Maker.
To carry out an attack on an ATM, a criminal needs to gain access to its USB port.
After that, you need to consistently use a number of software tools.
The Cutlet Maker includes a special Stimulator module that displays the number and denomination of banknotes in ATM cassettes.
This allows an attacker to initially select the cell containing the largest amount of money, and not act "blindly", going through the cassettes one by one.
Thus, the time to carry out an attack is reduced, and, consequently, the chances of catching criminals at the scene of a robbery are reduced.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that the Cutlet Maker malware is offered to anyone on the underground Internet market.
The malware costs $ 5,000, and the kit includes step-by-step instructions.
Thus, even the most inexperienced intruder can commit a crime.
It is not yet clear who exactly is behind the development of Cutlet Maker.
But analysis shows that for malware creators english language is not native.
Apple may block smartphones with non-original displays
With the release of iOS 11.0.3, Apple has the ability to block smartphones and tablets with a non-original display installed.
Consequently, now the "apple" manufacturer can remotely control devices and track what components are used in them.
Apple commented on the update:
“Resolved an issue with touch input not working on iPhone 6S, resulting in some devices not responding to touch after receiving counterfeit parts.
Replacing defective displays with non-genuine displays can result in degraded picture quality and malfunction.
Apple certified repairs are carried out by experts using genuine parts. "
Previously, iPhone 6S owners have received complaints about display defects.
Some users have repaired their gadgets not at certified service centers.
At some point, their touch input stopped working.
Then Apple released an update, fixing the problem remotely.
Also, the manufacturer strongly recommended that the iPhone be repaired only at authorized service centers.
Thus, at some point, millions of iPhones, iPads and other Apple products may stop working if they have been repaired by third-party specialists.
Antivirus has appeared in Chrome for Windows
Google released new version desktop chrome browser for Windows.
The update brings built-in anti-malware capabilities.
So, now Chrome determines whether the browser settings have been changed without the knowledge of the user and offers to return the settings to the previous form in case of changes.
Also, a kind of built-in antivirus appeared in the browser.
It will offer to remove any suspicious or malicious program from the PC, including during the silent installation.
The ESET engine is used to detect malware.
The update began to roll out gradually for chrome users for Windows.
A lot of computer users often ask themselves what is RAM. To help our readers understand RAM in detail, we have prepared a material in which we will consider in detail where it is can be used and what his types are now used. We will also look at a little theory, after which you will understand what modern memory is.
A bit of theory
The abbreviation for RAM stands for - random access memory... Basically, it is the RAM that is mainly used in your computers. The principle of operation of any type of RAM is built on storing information in special electronic cells... Each of the cells is 1 byte in size, that is, it can store eight bits of information. Each electronic cell has a special address... This address is needed in order to be able to access a specific electronic cell, read and write its contents.
Also, reading and writing to an electronic cell must be carried out at any time. In the English version, RAM is RAM... If we decipher the acronym RAM (Random Access Memory) - random access memory, then it becomes clear why reading and writing to a cell is carried out at any time.
Information is stored and rewritten in electronic cells only when your PC works, after turning it off, all the information that is in RAM is erased. The set of electronic cells in modern RAM can reach a volume of 1 GB to 32 GB. The types of RAM that are currently in use are called DRAM and SRAM.
- First, DRAM is dynamic random access memory, which consists of capacitors and transistors... Information storage in DRAM is caused by the presence or absence of charge on the capacitor (1 bit of information), which is formed on the semiconductor crystal. To save information, this type of memory requires regeneration... Therefore this slow and cheap memory.
- Second, SRAM is Static RAM... The principle of accessing cells in SRAM is based on a static flip-flop that includes several transistors. SRAM is expensive memory, so it is mainly used in microcontrollers and integrated circuits, which have little memory. it fast memory, not requiring regeneration.
Classification and types of SDRAM in modern computers
The most common type of DRAM memory is synchronous memory SDRAM... The first subtype of SDRAM is DDR SDRAM. DDR SDRAM memory modules appeared in the late 1990s. At that time, computers based on Pentium processes were popular. The image below shows a 512 MB DDR PC-3200 SODIMM bar from GOODRAM.
Prefix SODIMM means memory is for laptop... In 2003, DDR SDRAM was replaced by DDR2 SDRAM... This memory was used in modern computers of that time until 2010, when it was replaced by the next generation of memory. The image below shows a 2 gigabyte DDR2 PC2-6400 bracket from GOODRAM. Each generation of memory demonstrates an increasing rate of data exchange.

DDR2 SDRAM was replaced in 2007 by an even faster DDR3 SDRAM... This format remains the most popular to this day, although it breathes in the back new format... The DDR3 SDRAM format is now used not only in modern computers, but also in smartphones, tablet pc and budget graphics cards... Also, DDR3 SDRAM is used in the game console Xbox one eighth generation from Microsoft. This set-top box uses 8 gigabytes of DDR3 SDRAM RAM. The image below shows 4GB DDR3 PC3-10600 memory from GOODRAM.

DDR3 SDRAM memory type will be replaced by a new type soon DDR4 SDRAM... Then DDR3 SDRAM is waiting for the fate of past generations. Mass memory release DDR4 SDRAM started in Q2 2014 and is already being used on motherboards with a cpu socket Socket 1151... The image below shows the format bar DDR4 PC4-17000 4 gigabytes from GOODRAM.

DDR4 SDRAM bandwidth can be up to 25 600 Mb / s.
How to determine the type of RAM in a computer
Determine the type of RAM that is in the laptop or in desktop computer can be done very easily using the utility CPU-Z... This utility is completely free. Download CPU-Z can be obtained from its official website www.cpuid.com. After downloading and installing, open the utility and go to the " SPD". The image below shows the utility window with open tab « SPD».
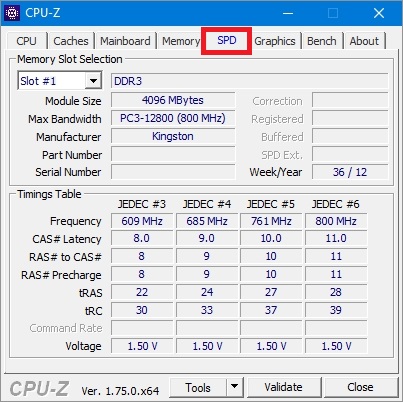
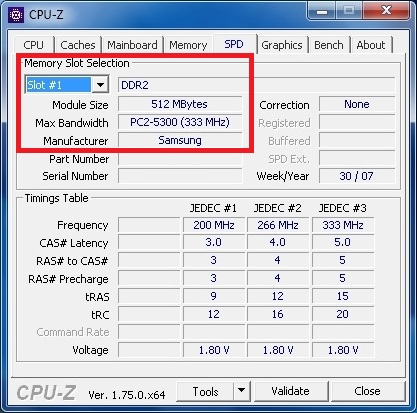
In this window, you can see that the computer on which the utility is open has RAM of the type DDR3 PC3-12800 4 gigabytes from Kingston. In the same way, you can determine the type of memory and its properties on any computer. For example, below is a window CPU-Z with RAM DDR2 PC2-5300 512 GB from Samsung.
And this window shows a window CPU-Z with RAM DDR4 PC4-21300 4 GB from ADATA Technology.

This method of checking is simply irreplaceable in a situation when you need to check for compatibility the memory you are about to purchase for rAM expansion your PC.
We select the RAM for the new system unit
In order to select RAM for a specific computer configuration, we will describe an example below, which shows how easy it is to match RAM to any PC configuration. For example, we will take this latest Intel processor-based configuration:
- CPU - Intel Core i7-6700K;
- Motherboard - ASRock H110M-HDS on Intel H110 chipset;
- Video card - GIGABYTE GeForce GTX 980 Ti 6GB GDDR5;
- SSD - Kingston SSDNow KC400 1000 GB;
- Power Supply - Chieftec A-135 APS-1000C 1000W.
To select the RAM for such a configuration, you need to go to the official page of the ASRock H110M-HDS motherboard - www.asrock.com/mb/Intel/H110M-HDS.
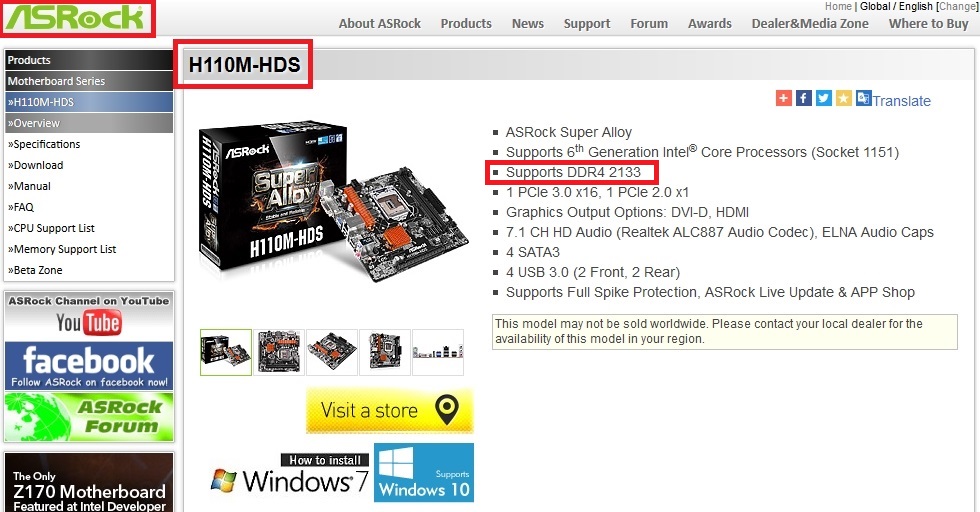
The page contains the line “ Supports DDR4 2133", Which says that a 2133 MHz RAM is suitable for the motherboard. Now let's go to the menu item " Specifications" on this page.
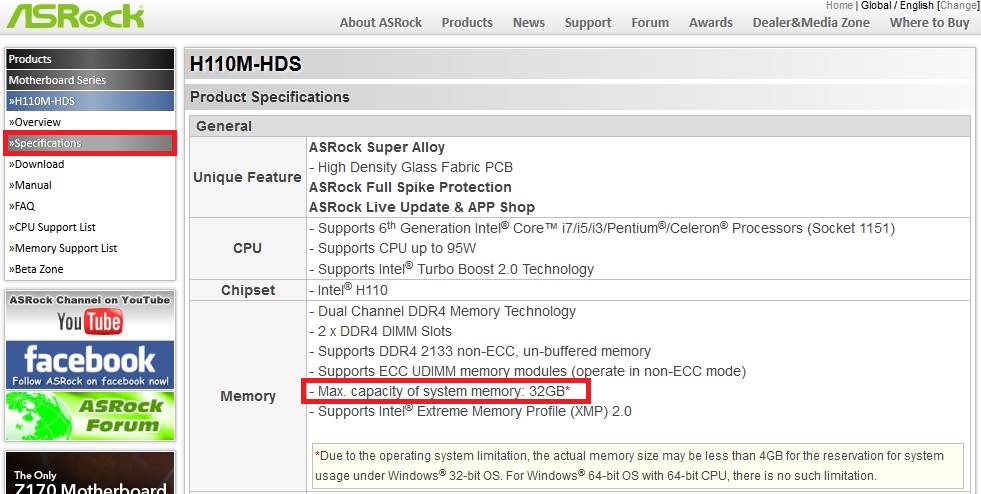
On the page that opens, you can find the line “ Max. capacity of system memory: 32GB”, Which states that our motherboard supports up to 32 gigabytes of RAM. From the data that we received on the motherboard page, we can conclude that this type of RAM would be an acceptable option for our system - two DDR4-2133 16 GB PC4-17000 memory modules.
We have specifically indicated two 16 GB memory modules, and not one 32 GB, since two modules can work in dual channel mode.
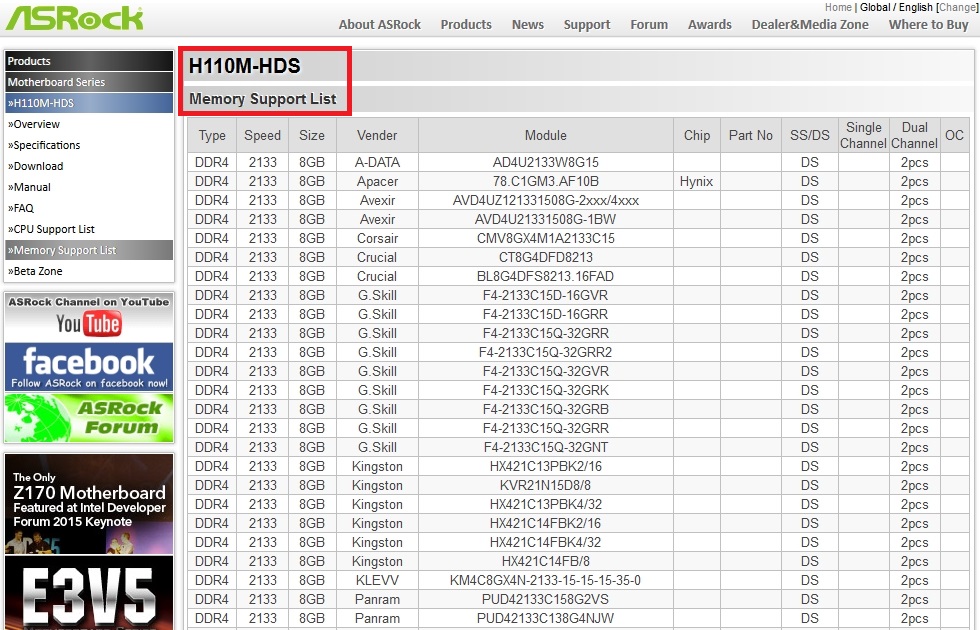
You can install the above modules from any manufacturer, but these RAM modules will work best. They are presented on the official page for motherboard in point " Memory Support List", As their compatibility has been verified by the manufacturer.
The example shows how easy it is to find out information about the system unit in question. In the same way, RAM is selected for all other computer configurations. I would also like to note that on the configuration discussed above, you can run all newest games with the highest graphics settings.
For example, on this configuration, new games such as Tom clancy's the division, Far cry primal, Fallout 4 and many others, since such a system meets all the realities of the gaming market. The only limitation for such a configuration would be its price... The approximate price of such a system unit without a monitor, including two memory modules, a case and components described above, will be about 2000 dollars.
Classification and types of SDRAM in video cards
Newer graphics cards and older models use the same type of synchronous SDRAM. In new and outdated models of video cards, this type of video memory is most often used:
- GDDR2 SDRAM - up to 9.6 GB / s bandwidth;
- GDDR3 SDRAM - up to 156.6 GB / s bandwidth;
- GDDR5 SDRAM - up to 370 GB / s bandwidth.
To find out the type of your video card, the amount of its RAM and the type of memory, you need to use free utility GPU-Z... For example, the image below shows the program window GPU-Z, which describes the characteristics of the video card GeForce GTX 980 Ti.
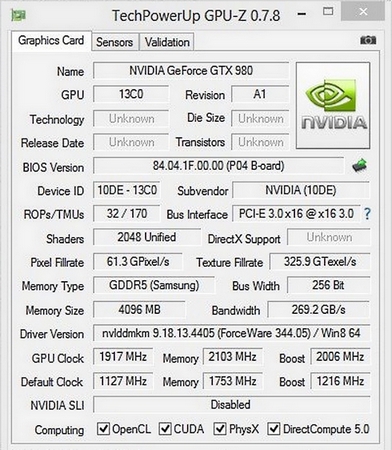
The popular today GDDR5 SDRAM will be replaced in the near future by GDDR5X SDRAM... This new video memory classification promises to raise bandwidth to 512 GB / s... The answer to the question of what manufacturers want to achieve from such a large throughput is quite simple. With the advent of formats such as 4K and 8K, as well as VR devices, the performance of current video cards is no longer enough.
Difference between RAM and ROM
ROM stands for read-only storage... Unlike RAM, ROM is used to record information that will be stored there permanently. For example, ROM is used in such devices:
- Mobile phones;
- Smartphones;
- Microcontrollers;
- BIOS ROM;
- Various household electronic devices.
In all the devices described above, the code for their operation is stored in ROM. ROM is an non-volatile memory, therefore, after turning off these devices, all information will be saved in it - which means this is the main difference between ROM and RAM.
Summing up
In this article, we briefly learned all the details, both in theory and in practice, concerning random access memory and their classification, and also considered what is the difference between RAM and ROM.
Also, our material will be especially useful for those PC users who want to know their type of RAM installed in the computer, or find out which rAM needs to be applied for different configurations.
We hope our material will be interesting for our readers and will allow them to solve many problems related to RAM.
Related Videos
