In a computer and why is it needed? It seems like there is a big hDDthat can store a lot of data. And then there is some kind of difference between them is that the first stores information for a long time, and even when the power is turned off, it does not disappear anywhere. But the second of them is fast memory, which contains only what the processor is currently working with. In the event of a power outage, it is completely reset to zero, that is, it is volatile. Now let's take a closer look at what is RAM in a computer.
What it is?
First, let's figure out what RAM is in a computer. Given as follows: "O" - operational, "Z" - storage, "U" - device. Physically, this is a very fast memory, which stores information being processed at the current time. The basic unit of measurement is a byte, consisting of 8 bits. Each of them can store only one value: "0" (no signal) or "1" (potential present). Now RAM is measured in gigabytes. Basic PC models are equipped with 4GB, and more advanced ones - 8 or more. It is installed in expansion slots as separate cards.
We clean
After we figured out what RAM is in a computer, let's figure out how to clean it. And here two options are possible. In one case, this is the removal of dust from the memory strip. To do this, we disassemble the case and find them. We remove them and blow them lightly with a fan, wipe them with a dry cloth. Then we wipe the contact group with gauze moistened with alcohol to remove the oxide film and allow time for it to dry. In the same way, it is recommended to clean the rest of the PC expansion modules every six months.
And in the second case, how to clean the RAM on a computer means stopping unnecessary processes. To do this, go to "Start", then to "Control Panel". Here we find "Administration" and the shortcut "Services". In the window that opens, select the service you want by clicking the left mouse button and then clicking the button with a square on the toolbar. It is important to understand that all services cannot be stopped and before performing this operation, you need to make a list of those with which you can perform actions.

Install
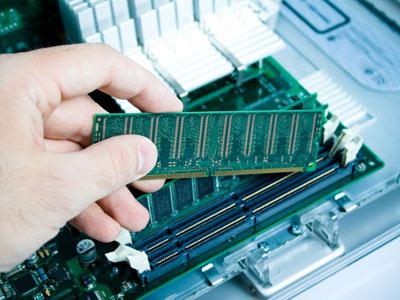
Now let's figure out how to install RAM in a computer. First you need to study the documentation for your computer. Rather, to clarify the number of provided installation places and the maximum supported amount of RAM. All this is in the manual for the motherboard or laptop. Next, we clarify the size of the installed modules. To do this, when loading, we hold down Del or F2 (this can be found out at the start of the download in the message: Press x to setup, where x is the key we need). After entering the BIOS, go to its main page MAIN. Here you need to find the Installed memory item. Opposite it there will be a number - this is the amount of RAM in megabytes.
Now we compare the resulting value with the one indicated in the documentation. If they are the same, then no more modules can be installed. Otherwise, we find out the type of supported memory. For example, DDR3 with a frequency of 1866 (this information is in the user manual). Then we buy a new module with a large volume (if all slots are occupied) or new board with the same amount of memory (assuming free footprints). In the first case, we remove the bar and install a new one, and in the second, we simply put it in a free slot.
Conclusion
This article described what RAM is in a computer and why you need it. Despite the fact that it is considered more important to buy a more efficient processor or a powerful gaming video card, you should not forget about RAM either. Its lack can lead to the fact that applications will slow down. Any modern computer must be equipped with a minimum of 4 GB. If it is planned to solve more serious problems, then its size should be doubled - 8 GB.
First you need to understand the principle of action and define the concepts. Let's take a closer look at what is RAM in a computer and on others mobile devices... To understand the difference between temporary storage of data in RAM and storage on a hard disk, you need to understand how they work.
RAM. What is it?
Random access memory (RAM for short) is one of the most important components of the technical architecture of a computer. The system cannot work without this component. The RAM module is responsible for the speed of operations performed on the PC, as well as for the overall processing speed of the device. The larger the amount of RAM, the more threads the processor can accept and issue. Serves rAM for short-term storage of information in order to carry out operations during the current session of the computer.
it general information about what RAM is.
What is RAM for and how is it different from ROM (hard disk)?
Technically, RAM is a system component that stores information only as long as the computer is turned on and the RAM module is receiving power. When you turn off the computer or if there is a power failure, the data in the RAM is erased.

This is the main difference between RAM and ROM and removable media, in which information is stored permanently and is not cleared when turned off. RAM acts as a transfer link between the computer's processor and ROM. This was done in order to maximize the speed of the system. During a session, RAM is loaded required files... This significantly increases the speed of work.
A hard disk stores information on a mechanical medium that does not depend on a constant power supply, but the data processing speed on it is much lower than on a RAM module. If the computer's operations were performed using ROM, then the system would be extremely slow. RAM, on the other hand, processes streaming signals many times faster, although it requires maintenance constant voltage... RAM is also accessed by other system devices, for example, a video card, sound card... When working on the Internet, browsers also use RAM, loading site pages into it. Essentially, all processes running on a computer are handled through RAM. Now we have figured out what RAM is. We also figured out how it differs from ROM. What is RAM in a laptop? The principle of operation is the same, only the modules are more compact.
 The processed data can be saved or edited on the hard disk through various user programs and interfaces. The transfer of impulses between the main memory and the central processor is carried out using the system bus.
The processed data can be saved or edited on the hard disk through various user programs and interfaces. The transfer of impulses between the main memory and the central processor is carried out using the system bus.
What is RAM memory on mobile devices?

Today, portable devices are becoming increasingly popular - smartphones, phones, tablet PCs. These devices also require RAM to operate. What is RAM in a phone? Principle of operation modern phones and tablets are similar to those of a regular computer. Therefore, the answer to the question of what is RAM in a computer is almost universal. It is enough to understand the principles of operation of one device.  For example, you need to find out what RAM is in a tablet or in a smartphone (phone). In these devices, RAM is also a system buffer for processing information when working with applications and interfaces when the device is turned on, which is also cleared when the device is turned off. But when wondering what RAM is in a smartphone or phone, one difference needs to be taken into account: the number of system and service processes that are performed on a mobile platform is less than on a full-fledged computer. With less RAM than a PC, a smartphone or tablet can handle resource-intensive programs (various editors, work with video, games).
For example, you need to find out what RAM is in a tablet or in a smartphone (phone). In these devices, RAM is also a system buffer for processing information when working with applications and interfaces when the device is turned on, which is also cleared when the device is turned off. But when wondering what RAM is in a smartphone or phone, one difference needs to be taken into account: the number of system and service processes that are performed on a mobile platform is less than on a full-fledged computer. With less RAM than a PC, a smartphone or tablet can handle resource-intensive programs (various editors, work with video, games).
Also, using RAM, the startup sequence is determined system services, the execution priorities of user applications are set and the current workflows on the device are regulated. On devices with an operating room android system these manipulations are carried out in the settings, their work is regulated using the task manager. This is basic information about what RAM is in a phone and other modern mobile platforms. 
RAM appearance
On ordinary personal computers, RAM modules are installed in the corresponding slots (connectors) on the motherboard. They themselves are small microcircuits and differ in shape, standard and volume. They also produce more powerful ones technical specifications memory circuits. They are used where the maximum processing speed is required. These types of RAM do not look like regular custom modules. During active work, they get very hot, and therefore manufacturers equip them with a forced cooling system. This preserves the declared performance on high-frequency processes and the stability of the RAM memory.
Varieties of random access memory
By type, there are 2 types of RAM that are used on computers and other devices: static type (SRAM) and dynamic type (DRAM). They work on semiconductor materials. Access to any part of such RAM is carried out arbitrarily by referring to its unique address.
Static memory (SRAM)
Has high performance due to the use of special circuits of the executive semiconductors. However, with visible advantages, there are also disadvantages, for example, it requires a lot of space for placement. In addition, this type of memory is expensive. Therefore, SRAM is used to store a small amount of short-term cache memory on the processor chipset and other computer devices. To dwell especially on this kind of memory in this review we won't.
Dynamic memory (DRAM)
Most computers use this type of RAM as the RAM. The principle of operation using capacitors is applied here, data processing is carried out at high frequencies. The cost of such RAM is relatively low. Dynamic memory also has disadvantages. They are connected with the DRAM technical device. The capacitors used in these modules have low internal capacitance. This leads to them fast discharge and the need for timely recharge (regeneration). Periodic memory refresh slows down system performance. Therefore, developers are looking for technical solutions to speed up work. For this purpose, special schemes have been created. Their use stabilizes memory and minimizes delays for regular volume replenishment.
Information processing speed in RAM
Random access memory is subdivided by data processing speed. One of the first types of RAM was DDR SDRAM. Its feature was the doubled speed of execution of operations. It is now outdated and does not apply. It was replaced by DDR2 SDRAM. On this sample, the operating bus frequency was doubled. The peak frequency reached 1200 MHz.
Mostly DDR3 memory is used now. It was designed to reduce power consumption while increasing memory performance and speed, as well as doubling its operating frequency. Modules of different generations are technically and mechanically incompatible with each other. What is RAM of the future? Great hopes are pinned on the next generation of RAM - DDR4. The creators are working on technical improvements: lowering energy consumption and cost, increasing speed and efficiency.
What else determines the speed of your computer?
The totality of all the hardware components of a computer is an important factor in the performance of the entire system. You can install the fastest memory, but if some element of the technical architecture cannot cope with high speeds, then the overall speed of work will slow down.
In modern devices, to improve work efficiency, they began to install internal memory... This allows you to quickly operate with data and offload RAM. Some powerful video cards have their own acceleration modules, as well as new hard disks Equipped with a clipboard for fast work. However, these are just additional funds to the main RAM module.
Computer memory is needed to be able to run it at all. Operational or RAM is the main type of computer.
It stores running programs and information that you use. At the same time, all RAM is lost upon reboot, so if you need this data, you need to save it on your hard disk or other storage medium.
Important parameters of computer RAM and how to choose it
How to choose RAM for your computer? As already mentioned, it is of paramount importance to ensure the health of your computer.
Much depends on the amount of RAM that the computer or laptop ultimately gets.
More RAM is better for the user. The computer will then run faster. There are two main types currently on the market: DDR2 and DDR3.
The type of RAM must be adapted to the motherboard - not every one supports both types of chips, and both cannot be used at the same time.
DDR3 SDRAM is manufactured in 90nm process technology and has a standard supply voltage of 1.5V. The DDR2 standard requires a voltage of 1.8V.
DDR3 memory modules are equipped with 240 pins, exactly the same number as DDR2, but a controller designed for DDR2 will not work in DDR3.
Depending on the type of application, the RAM can be divided for ordinary users, gamers, enthusiasts, professionals and laptops.
The RAM must be adapted to the specific type of processor: Intel or AMD.
If you have an Intel with 200 or 266 MHz FSB, you should choose the DDR system, with the corresponding 800 or 1066 MHz.
The choice of DDR3 is justified for the LGA 775 platform if your computer will operate on a bus over 333 or 1333 MHz.
If your PC has aMD processorthen it works on Socket AM2 / AM2 + DDR2 systems.
The best choice of memory for it is DDR2-1066, it will be efficient and you can even overclock the processor performance.
When choosing RAM, not only its size is important, but also its performance. It includes: frequency and channel set.
The operating frequency determines the performance. Fast RAM improves the performance of the entire platform.
It also affects the processing power of the processor. The higher it is, the better. It is specified in MHz and can be 800 or 1066 MHz.
The latency parameter affects the duration of individual cycles and is of particular importance in DDR2.
DDR3 is not that sensitive to latencies and its operation is mainly determined by the frequency. The lower the latency, the better; they provide improved efficiency regardless of other parameters of your computer system.
The RAM can use Dual Channel or three-channel solutions. Then the controller will receive data streams from two or three modules simultaneously.
Dual channel or triple mode can be used in the latest module kits of various capacities.
The RAM of the cooler is also necessary for the proper functioning of the entire system.
In most cases, ordinary aluminum radiators are used for this purpose, which are located on either side of the module.
Computer RAM manufacturers and their products
There are several well-known RAM manufacturers: Kingston, Goodrem, OCZ, A-Data, Patriot, Corsair, Kingmax, etc. The type of module (DDR2 or DDR3), and the power of the chips affects the prices.
Frequently asked questions before choosing
- How much RAM is sufficient
The choice is highly dependent on the goal. If your computer is designed for office tasks: sending and receiving email or work on the Internet, then 1-2 GB is enough for you.
- How much RAM do you need for multimedia applications
If you are going to watch movies on your computer in high definition video or play the latest games, then you will need at least 2 GB.
- Which DDR2 or DDR3 to Choose
Previously, only intel processors... Today, thanks to the advent of AMD AM3, DDR3 can be used in them as well.
If you care about the most up-to-date technology and you have an adequate budget, then invest in DDR3.
- How much RAM is sufficient
In general, there is a rule that the higher its capacity, the more programs can work simultaneously.
However, it all depends on the individual needs and requirements of the users. You can choose from 512 MB, 1, 2, 4 or 8 GB chips.
- How much RAM do you need for Windows XP and Windows 7
For Windows XP, you should have at least 1 GB, but for people who want to play modern games, 4 GB hardware is recommended.
When it comes to Windows 7, and it should be able to run multiple programs at the same time, make sure you have at least 2GB.
- What type to use
The type depends on the installed motherboard. Therefore, before choosing, refer to the instructions that came with the motherboard and see which one it supports.
If you do not have this manual, you can diagnose the hardware (using free programs), which will give you the answer to this question.
You should always pay attention to the performance, clock speed and access time presented to keep it as short as possible.
Also, RAM must correspond to the connectors on the computer's motherboard, it will be connected through it. Good luck.
If your computer becomes slower, additional RAM may be the solution. In this case, you need to figure out what RAM is and what it is for, find out its parameters, and also read the recommendations for installing and replacing this module.
What is RAM?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is also called:
- RAM (Random Access Memory);
- random access memory;
- or just RAM.
Photo: Random Access Memory
RAM is a volatile computer memory that has random access. During computer operation, it is there that all intermediate, input and output data that the processor processes are stored. All data on RAM can be accessed and saved only when the device is powered. Even with a short-term power outage, information can be distorted or completely destroyed.
Data exchange between Random Access Memory and the processor takes place:
- directly;
- through registers in ALU;
- through the cache.
OP is:
RAM usage
Operating systems for information processing, as well as data storage, which are often used, use random access memory. If modern devices did not have Random Access Memory, then all operations would be much slower, since it would take much longer to read information from a permanent memory source.
Also, multithreading would be impossible. Thanks to the presence of the OP, all applications and programs start and run faster. At the same time, nothing complicates the processing of all the data that is in the queue. Some operating systems, such as Windows 7, have the ability to store files, applications, and other information that the user frequently uses in memory.
Thus, there is no need to waste time while they start to boot from disk, since the process will start immediately.
As a rule, because of this, Random Access Memory will be constantly loaded by more than 50%. This information can be viewed in the task manager. Data has the ability to accumulate and those applications that are used less often will be replaced by more necessary ones.

By far the most common is dynamic random access memory (DRAM). It is used in many devices. At the same time, it is relatively inexpensive, but it works slower than static (SRAM).
SRAM has found its way into controllers and video chips, and is also used in processor memory caches. This memory has more high speedhowever, it takes up a lot of space on the crystal. In turn, manufacturers decided that volume is much more important than accelerated work, so DRAM is used in computer peripherals. In addition, dynamic memory costs an order of magnitude less than static memory. Moreover, it has a high density. This allows more memory cells to fit on the exact same silicon chip. The only drawback is that it is not so fast worklike SRAM.

It should be borne in mind that all the information that is contained on the OP can only be accessed when the device is turned on. After the user exits the program, all data will be deleted. Therefore, before exiting the application, you must save any changes or additions that have been made.
OP consists of several cells. This is where all the data is located. With each saved change, the latest information is deleted, and new information is written in its place. The number of cells depends on the size of the Random Access Memory. The larger this volume, the higher the performance of the entire system.
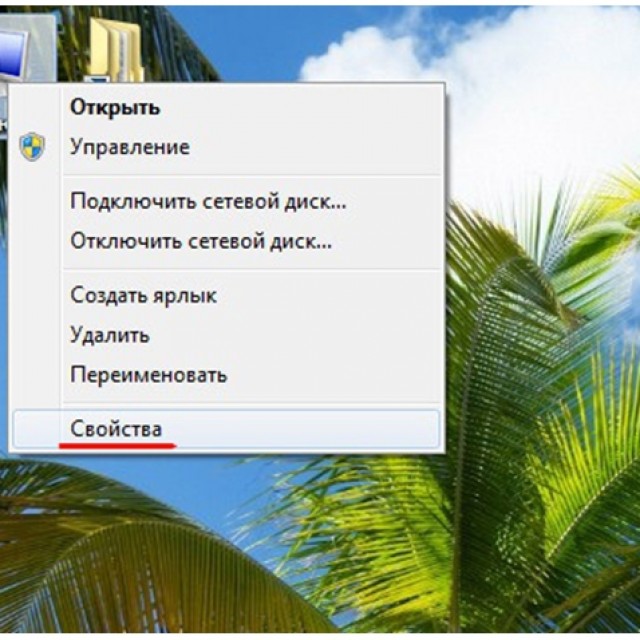
To find out the RAM of your computer, you need to do the following:
- for Windows XP:
- hover the cursor over the shortcut "My Computer";
- then you need to press right key mice;
- select "Properties";
- go to the "General" tab;
- for Windows 7:
Install
Additional OP will help to significantly improve the performance of the device. It can be installed both on a stationary computer and in a laptop.
Installing RAM on a computer
First you need to figure out what type of OP is required. Its type depends on the motherboard. In order to find out which type is compatible with the motherboard, you should check the documents for the device or visit the manufacturer's website. When choosing RAM, it is recommended to purchase 2 or 4 modules. Thus, if you need 8 GB of RAM, then it is better to buy 2 x 4 GB or 4 x 2 GB. In this case, you should pay attention to their bandwidth and speed. All data must be the same. Otherwise, the system will adjust to the minimum parameters. This may cause performance degradation.

Photo: RAM installed
To install RAM, follow these guidelines:
- you need to disconnect the monitor, mouse, printer and keyboard from the device;
- make sure there is no static charge;
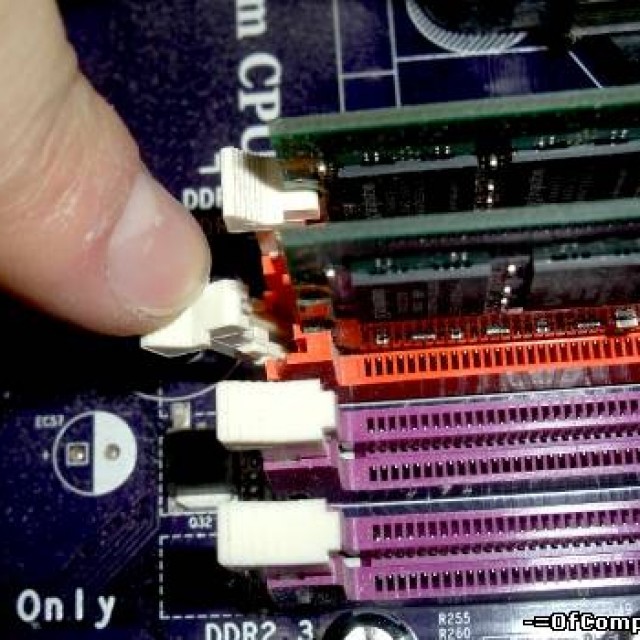
- remove old modules - for this you need to open the clamps located on both sides and remove the module;
Important! The new OP module should be held so as not to touch the microcircuits that are on the side and bottom contacts.
- The RAM must be inserted in such a way that the groove is exactly aligned with the protrusion located in the slot;
- press the board and fix it, while the clamps should close;
- build a computer;
- turn on the device;
- check for OP.
Installing RAM on a laptop
For this you need:
- correctly determine the type of OP;
- eliminate static charge;
- disconnect the laptop from the power supply and remove the battery;
- take off desired panel on the underside of the laptop;
Important! Most laptops do not require paired modules.
Type and volume
At the moment, there are several types of OP. It:
- DDR RAM;
- DDR2 RAM;
- DDR3 RAM.
They differ in the design of the bar, as well as in performance.

Important! It should be noted that the modules are completely incompatible with each other, since they have different connectors for mounting.
Most modern laptops have a DDR2 or DDR3 OP. Legacy models work with DDR. The speed and performance of the computer directly depends on the amount of RAM.
Now there are modules on the market with the volume:
- 512 MB;
- 1 GB;
- 2 GB;
- 4 GB;
- 8 GB.
Before purchasing additional modules, it is worth considering that 32-bit operating system will only be able to recognize 4 GB. Therefore, there is no need to spend money on boards with a large volume due to the fact that it will not be used anyway. But if the operating system has 64 bits for it, you can install 8, 16 or even 32 gigabytes of memory.
Video: increase RAM
Frequency and other parameters
Among the main parameters of Random Access Memory, the following should be highlighted:
- DDR - 2.2 Volts;
- DDR2 - 1.8 Volts;
- DDR3 - 1.65 Volts.
- module manufacturer. Preference should be given to well-known brands and models that have the greatest number positive feedback... This will help eliminate the possibility of buying a defective part, and the warranty period will be longer.
What does RAM look like in a computer?
The OP of a computer is a plate consisting of several layers of PCB. It contains:
- printed circuit board;
- soldered memory chips;
- there is also a special connector for connection.

Where is the RAM located? The OP is located directly on the motherboard.

There are slots for modules, usually 2 or 4. They are located next to the processor.
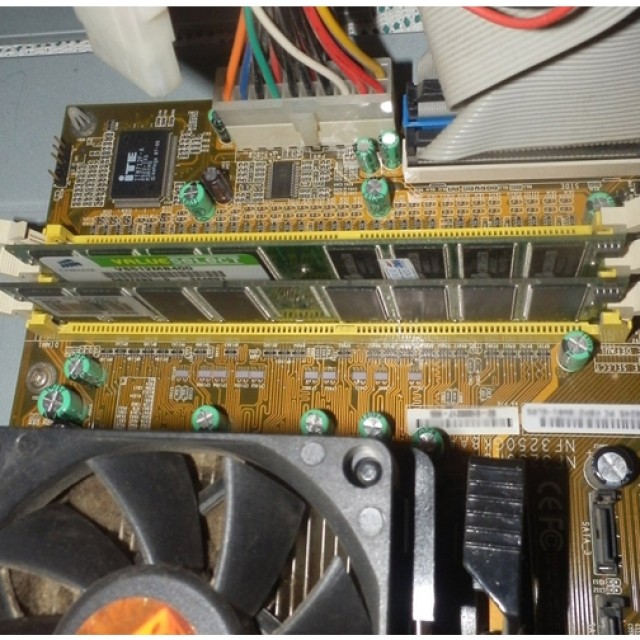
Photo: storage device on the motherboard
OP for PCs and laptops
The RAM intended for a laptop has several differences from the RAM used in a PC, namely:
- modules differ in their size - the plate for a laptop is much shorter than the standard one for a computer;
- the bracket also has unique connectors.
Thus, the module used for the PC cannot be installed in the laptop.
Random access memory is one of the main parts in a computer. She is responsible for the speed of launching various programs and applications, as well as for the temporary storage of information. In addition, with its help, communication is carried out external devices and hard disk with a processor.
So, the computer's RAM , which is also called volatile. It is also called DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) - dynamic random access memory or random access memory, abbreviated as RAM.
Let's see why it is called that way? During computer operation, all data and programs launched by the user are stored in RAM. The word "volatile" in relation to memory only means that when the power is turned off (shutdown), the computer's RAM is reset to zero. All of its contents disappear.
There is also non-volatile memory - this is your computer, because the data on it is saved even after the power is turned off.
"Dynamic random access memory": access (reference) to its different cells occurs in an arbitrary order and at different times, hence the definition. But with the word" dynamic"The situation is more complicated. Let's figure it out!
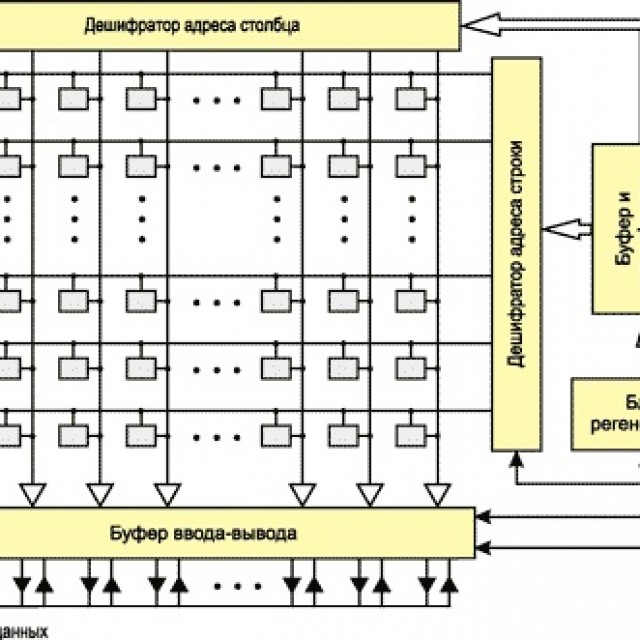
The smallest unit of the structure of a computer's RAM is a cell. An array of closely spaced cells is combined into conditional rectangular tables called matrices. The horizontal rulers of such a matrix are called rows, and the vertical columns. The whole rectangle of the matrix is \u200b\u200bcalled the "page", and the collection of pages is called the bank. All these things are a bit virtual, in the sense that, for example, a "bank" can be called a whole DIMM module or a separate part of it (memory chips located on one side of it).
In any case, the diagram of the structure of the computer's RAM (its fragment) can be seen in the picture below (click to enlarge):
As we said, the smallest unit at the physical level is the cell. The cell consists of one micro-capacitor (designated C in the diagram above) and three transistors (VT). The capacitor stores a small charge, and the transistors act as "keys", which, on the one hand, do not allow the capacitor's charge to spontaneously drain, and on the other hand, allow / prohibit access to the capacitor for reading or changing.
Each capacitor can store the smallest unit of information - one bit of data. If the capacitor is charged, then, according to the binary number system used in computers, it is a logical "one", if there is no charge - a logical "zero" and there is no data.
In theory, the scheme of organizing the operation of RAM looks nice, but there are no ideal solutions, and in practice, developers have to deal with the fact that the charge from the capacitor leaves the capacitor quickly enough or its partial spontaneous discharge occurs (the "keys" do not save the situation), so there is no other option exit, how to periodically recharge it. How often? Several dozen times per second! And this despite the fact that there are several million such capacitors in one memory chip!
As a result, the state of all memory must be constantly read and updated again in a short period of time (otherwise, all its data will simply disappear). That is why it got the name "dynamic", meaning its dynamic automatic update or regeneration. In the photo above, we can see its special blocks, which are responsible for this function.
You also need to take into account the fact that the process of reading in DRAM is destructive: after accessing any cell, its capacitor is discharged and in order not to lose the data contained in it, the capacitor must be recharged. The second "surprise" is that, due to design features, the decoder of the row / column address issues the command to read not one specific cell, but the entire row (or column) at once. The read data are completely stored in the data buffer and then the requested data are selected from them by the application. After that, you need to recharge immediately whole line cells!
Although it may seem that the regeneration (renewal) process is somewhat chaotic, it is not. The RAM controller takes a strictly regulated technological pause at regular intervals and at this time carries out a full cycle of regenerating all data.
Once I read a good phrase: "Dynamic memory can be compared to a leaky bucket. If it is not constantly replenished, then all the water will flow out!" Something conditionally similar is happening in the DRAM situation. Naturally, all these additional commands and charge-discharge cycles lead to additional delays in operation and are not a sign of high efficiency of the final product. So why can't you think of something more effective? Can! And it has already been invented - static random access memory (SRAM - Static Random Access Memory).
Static memory works much faster than dynamic memory by switching triggers and does not need to be regenerated. It is successfully used in building CPU caches and in frame buffers. Is it possible to organize the main system memory of a computer on the basis of SRAM? It is possible, but due to the complexity of the design, it will cost much more and it is simply not profitable for manufacturers :)
I think it's logical if we consider RAM dIMM type... The abbreviation stands for "Dual In-Line Memory Module" (double-sided memory module), and it is these boards that are still used in personal computers.
DIMM memory at the end of the 90s of the last century replaced the previous SIMM standard (Single In-Line Memory Module). In fact, the DIMM is a printed circuit board with printed on it contact pads... This is a kind of basis: memory chips and other electrical "strapping" are added by the manufacturer only later.
The fundamental difference between DIMM and SIMM, in addition to size, is that in the new standard the electrical contacts on the module are located on both sides and are independent, while in SIMM they are located only on one side of it (they are also found on two, but there they are simply looped and transmit, in fact, the same signal). The DIMM standard is also capable of implementing functions such as error detection and correction with parity check (ECC), but more on that below.
The computer's RAM is where cPU saves all intermediate results of its calculations and work, taking them back as needed for further processing. We can say that RAM is a working area for a computer.
Video cards are also happy to use the services of RAM (if they do not have enough to accommodate their data). does not have his own at all and without a twinge uses the operational.
Let's take a look at what regular DIMMs look like:
The computer's RAM is a multilayer textolite plate (in the photo - green and red, respectively). A printed circuit board (PCB) is a base with printed elements on it. A certain number of memory chips soldered into it (in the photo - four on each side) and a connection connector that is inserted into the corresponding slot on the motherboard.
The module slot actually determines the type of our DRAM (SDRAM, DDR, DDR2, DDR3, etc.). Take a closer look and you will see that in the photo the connector is divided in half by a small cut (it is called a "key"). It is this "key" that does not allow inserting a memory module into an incompatible slot on. Important : The "keys" on the module and on the board must match perfectly. This is a protection against incorrect installation in the board.
The diagram below shows the location of the "keys" for different types modules:

As you can see, all modules have the same length. Outwardly, the difference is only in the number of contact pads on the connector and the location of the "keys".
Now let's take a quick look at the most common types of RAM. Her different generations:
- SDRAM - (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory - synchronous dynamic random access memory). Module with 168 mu pins (contacts), powered by 3.3 Volts (V).
- DDR - (Double Data Rate - double data rate). Allows (unlike SDRAM) to sample (or transmit data) twice in one cycle of the memory bus. The module has 184 pins, its supply voltage is 2.6 V. With the advent of DDR memory, the previous generation of memory was called SDR SDRAM (Single Data Rate DRAM).
- DDR2 - the next generation of chips. It allows for one cycle to transfer already 4 bits of information (two sets of data) from the cells of the memory chips to the input-output buffers. PCB with 240 pins (120 on each side). Its supply voltage is 1.8 V.
- DDR3 - the next generation, capable of sampling 8 data bits, 240 contacts and a supply voltage of 1.5 Volts per clock cycle. At the same time, the power consumption of DDR3 memory is 40% less than that of DDR2, which is quite important when using it with mobile devices (laptops). Reducing power consumption is achieved by switching to a "thinner" process technology (90-65-50-40 nanometers).
- DDR4 - appeared on the market in 2014. Evolution of DDR3 (reduced voltage (1.2V), slightly more pins - 288, slightly higher module, transfer rate doubled due to twice the number of memory chips themselves). Data transfer rates up to 3.2 Gigabits per second. The maximum operating frequency of this type of memory is 4266 MHz
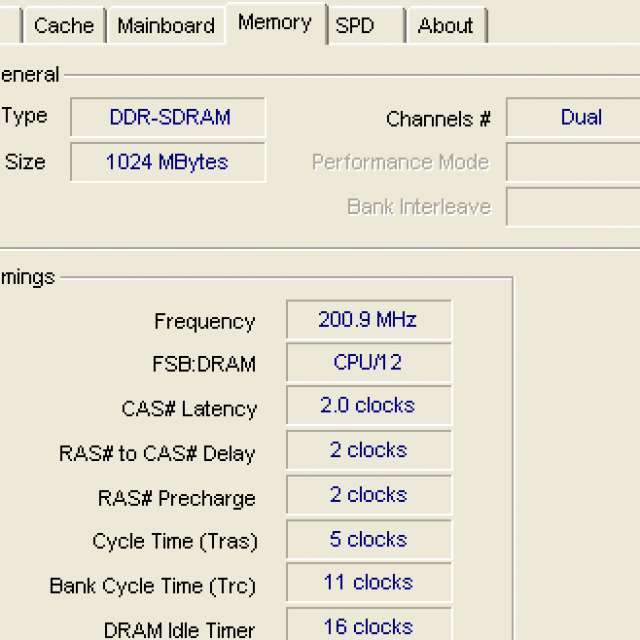
So, the signs that characterize the computer's RAM can be considered the following:
- RAM type (SDRam, DDR, etc.)
- Module volume
- The clock frequency of their work
- Timings (delays in accessing and fetching data from chips - latency)
We considered the first point above, but let's go through the rest. The volume of memory chips is now constantly increasing and now you will not surprise anyone with a 1 Gb (gigabyte) module. And before I well remember what awe the phrase aroused in me: "I have 128 megabytes of RAM installed on my computer!" And the acquaintance at that time was working with three-dimensional graphics in the "3DMax" modeling program :) Now there are modules of 16 gigabytes each and I am sure that this is not the limit.
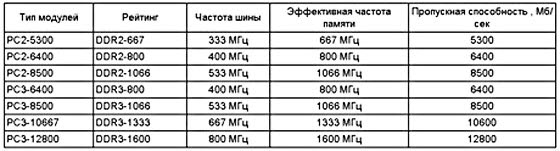
Moving on: clock speed. Measured in megahertz (MHz - MHz) and general rule is that the larger it is, the faster the memory works. For example, DDR4 memory is clocked at 4266MHz. At a higher frequency, the bandwidth of the RAM also increases (how much data it can "pump" through itself per unit of time).
Here's a small pivot table to illustrate this point:
Timings (latency) is a measure of the time delay between the arrival of a command in memory and the time it is executed. Latency is determined by timings, measured in the number of clock cycles between individual teams. Timings are adjusted in and by changing their values, you can achieve a certain increase in computer performance.
Taking this opportunity, I would like to add a small remark about all these "new" memory types: DDR2, 3, 4, etc. Roughly speaking, this is the same good old SDRAM module, but slightly altered. Since increasing the frequency of the memory itself is costly (no one likes to do this because of the inevitable heating that occurs after that), the manufacturers went for a trick.
Instead of a significant increase clock frequency the memory itself, they increased the capacity of the internal data bus (from memory matrix cells to I / O buffers) and made it twice as large as the width of the external bus (from the controller to memory chips). It turns out that as much data is read in one clock cycle as was previously read via the external bus in only two clock cycles. In this case, the width of the external data bus is, as before, 64 bits, and the internal one is 128/256/512, etc. bit.
Another "trick" that allows you to raise the speed without increasing the frequency is the parallel installation of modules to enable two and three-channel operating modes ( double and t riple-channel respectively). This increases the performance of the memory subsystem a little (5-10 percent). To work in this mode, it is preferable to use Kits. "KIT" is a set of modules, consisting of several "strips", which have already been tested to work cooperatively with each other.
On modern motherboards, slots (connectors) for memory through one are highlighted in different colors. This is done precisely to facilitate the installation of similar (ideally identical) modules in them. If the installation is successful, the multichannel mode will turn on automatically. The photo below shows boards with the ability to operate RAM in three and four-channel modes.

And this is how four channels of RAM may look like on the board ( quad-channel) :

Nowadays, multichannel memory modes are widely used. The idea is as follows: a dual-channel memory controller can simultaneously (in parallel) access each odd and even module. For example: the first and third modules transmit and receive data simultaneously with the second and fourth. In the traditional approach (single-channel mode), all installed modules were serviced by one controller (channel), which had to quickly switch between them.
The overall speed of each channel is determined by the slowest DIMM it contains. Also, try to adhere to the recommendation that: in each of the channels, you need to install strips of the same volume.
Now a few words about random access memory chips (chips). Like any element of a computer to which voltage is applied, the memory heats up. As we remember, the components inside system unit are fed by a certain amount, which is given to them - 12V, 5V or 3 Volts.
The microcircuits themselves are heated directly. And some board manufacturers put small radiators on their products to remove heat. Radiators, as a rule, are simply glued with a special compound or held on with thermal paste.

The radiator can also be snapped in at the top:

For example, here is a sample of computer RAM from the brand company "OCZ" in my home collection:

Thing! A double heatsink, the board is pleasantly heavy in the palm and generally gives the impression of being made to last. Plus - reduced work timings :)
I remember in 2008 I worked for a large company for some time. Everything was computerized there quite seriously. In the IT department they worked there, in a good sense of the word, real "maniacs" of their business :) When I first looked at the properties tab of the local server, which was running 64-bit Windows Server 2003, I was very surprised, to put it mildly. I saw a figure of 128 (one hundred twenty eight) gigabytes of RAM! Realizing that I looked stupid, I still decided to ask again, is this so? It turned out that this is indeed the case (128 gigabytes of DRAM). It's a pity that I was not able to take a look at that motherboard then :)
Let's continue! Memory chips can be located both on one side of the PCB printed circuit board, or on both, and be of different shapes (rectangular or square), installed as planar or as components. The height of the module itself can also be different. Each of the RAM chips has a certain capacity, measured in megabytes (now - in gigabytes).
For example, if our bar has a volume of 256 megabytes and consists of 8 chips, then (divide 256 by 8) and we get that each microcircuit contains 32 megabytes.
I cannot ignore a special class of memory - server DRAM. The photo below shows several modules: the first and third are server options (you can click on the photo to enlarge).
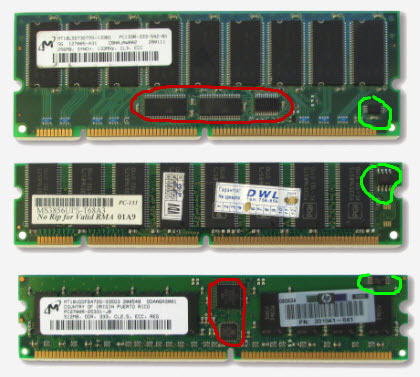
How does server memory differ from ordinary memory? Even visually, the photo above shows that server solutions have additional chips on the board, which provide it with additional functionality. Which one? Let's see! First of all, let's find out what additional components are on printed circuit board RAM (other than the RAM chips themselves) are standard? This is a series of solid-state tantalum SMD capacitors located directly above the contact pads of the module. These are the components of the memory card "binding".
The second required element (in the photo above it is marked in green) is the SPD chip. The abbreviation stands for “ Serial Presence Detect " - sequential detection interface or sequential presence detection. Something like this :) In fact, this is a programmable ROM, in which the settings of each memory module are "wired": all parameters, frequencies, timings, operating modes, etc. It is from there that when the computer starts, they are read by the BIOS chip.
Additional microcircuits on server boards (circled in red) provide the ability to detect and correct read / write errors (ECC technology) and partial buffering (memory register).
Note: ECC - (error-correcting code) Algorithm for detecting and correcting random errors in data transmission (no more than one or two bits per byte).
To implement these possibilities, an additional memory chip is installed on the module and it becomes not 64-bit, like ordinary DIMMs, but 72-bit two. Therefore, not all motherboards can work with similar memory. Some, we must give them their due - work! :)
Click on the photo above and you can see additional designations on the sticker (highlighted in red), which are not available for conventional memory. I am referring to abbreviations like SYNCH, CL3 (2.5), ECC, and REG. Let's dwell on them separately. Since the first of the modules shown in the photo refers to the distribution period personal computers under the general brand "Pentium", then the designation "SYNCH" is separately present on it.
Remember how the first letter of the SDRAM abbreviation stands for? Synchronous DRAM. A type of DRAM that works so fast that it can be synchronized in frequency with the operation of the RAM controller. At that time it was a breakthrough! Previous generations of RAM operated in asynchronous data transfer mode. Now, the commands could enter the controller in a continuous stream, without waiting for the previous ones to be executed. On the one hand, this reduced the total time for their transmission, but on the other hand (since the commands could not be executed at the speed of their arrival), there appeared such a concept as latency - execution delay.
The second indicator on the CL3 sticker tells us exactly about the latency of the server memory module. It stands for "Cas Latency" - the minimum time, measured in system bus cycles, between the read command (CAS, in fact - the transfer of the desired row or column address to memory) and the start of data transfer.
Another thing is that marketers even here try to fool us and indicate only one (the smallest) of all possible delays. In fact, there are quite a few types of timings, and this is logical: the organization of work on transmitting, fetching and recording data in such a large array is so complicated that it would be strange if there were no delays in memory work at all or the matter was limited to one!
For example, some (not all) delays are presented in the table below:

Thus, by specifying the latency value for only one parameter (CL) with the lowest indicator and not giving an idea of \u200b\u200bthe memory latency during other operations, they are trying to sniff us this case! I will not argue that this is happening, but the feeling arises exactly like this :)
We have already considered the designation ECC above, we will not repeat it. But let's deal with the "REG" pointer! As a rule, this is how Registered RAM modules are designated. What does it mean? An additional microcircuit is installed between the RAM chips and the bus, which acts as a kind of buffer. Therefore, this type of register memory is often referred to as Buffered or Partially Buffered.
The presence of special registers (buffer) on the memory module reduces the load on the synchronization system (electrical regeneration), unloading its controller. Registers are relatively quick to store incoming data that is often required by an application. The presence of a buffer between the controller and the memory chips results in an additional one clock cycle delay, but this is normal for server systems. We get higher reliability due to a small drop in performance.
The RAM for laptops is called SO-Dimm and has, for obvious reasons, a shortened design. It looks like this:

It is much more compact than its desktop counterpart, but it also has a unique "key". Remember: by the position of the "key" you can determine the type of microcircuit. Well, also - according to the inscription on the sticker (sticker) :)
And finally: buy RAM from reputable manufacturers: Samsung, Corsair, Kingston, Patriot, Hynix, OCZ and then they will bypass you.
Below you can take a short walk through the factory of one of the major manufacturers of DRAM chips - "Kingston".
