Multi-core processor - cPUcontaining two or more computing cores on one processor chip or in one package.
Among the multi-core processors at this point, one can distinguish
* processors designed mainly for embedded and mobile applications, in which developers paid much attention to means and methods for reducing power consumption (SEAforth (SEAforth24, seaforth40), Tile (Tile36, Tile64, Tile64pro), AsAP-II, CSX700);
* processors for computing or graphics stations, where power consumption issues are not so critical ( gPUs, for example, NVIDIA's g80 series processors, Intel's Larrabee project, the Cell processor from IBM can be partly included here, although the number of cores is relatively low);
* processors so-called. mainstream - designed for server, workstations and personal computers (AMD, Intel, Sun);
- The number of cores (The number of cores. The core is a silicon crystal with an area of \u200b\u200babout one square centimeter, on which a schematic diagram of the processor, the so-called architecture, is implemented through microscopic logic elements. Each core is perceived by the system as a separate, independent processor, with all the necessary set of functions. )
Clock frequency (a cycle is an elementary operation per second that a processor can perform. Therefore, the number of cycles is a measure of how many operations per second of time the processor can process. The unit of this parameter is gigahertz GHz.)
Cache memory (memory directly embedded in the processor and used to store and access frequently used data is called cache memory. It is divided into several levels - L1, L2 and L3. The higher level of cache memory has a larger amount, but less high-speed data access.)
Bit depth (determines the amount of information that can be exchanged between the processor and the RAM in one clock cycle. This parameter is measured in bits. The bit width parameter affects the amount of possible random access memory - A 32-bit processor can only work with 4GB of RAM.)
Performance
Power consumption
Dimensions
The cost
Classes of tasks for which they are designed
Comparative characteristics of processor performance, power consumption and data exchange rates are presented in tables
(Mflops is one million floating point operations per second)
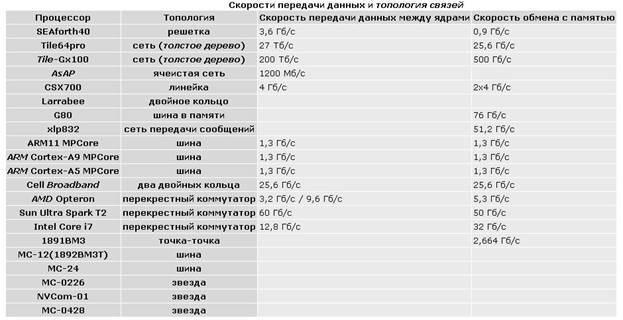
The structure of inter-core connections and the organization of the memory subsystem, in particular, cache memory, also make a significant contribution to the overall performance of the processor and its efficiency.
CSX700 processor
The CSX700 processor architecture was designed to address the so-called Size, Weight and Power (SWAP) problem, which is typically central to embedded high-performance applications. By integrating processors, system interfaces, and on-board error-correcting memory, the CSX700 provides a cost-effective, reliable and powerful solution to meet the demands of today's applications.
The processor architecture is optimized for massive data parallelism and is designed with a high degree of efficiency and reliability. The architecture focuses on intelligent signal processing and image processing in the time and frequency domains.
The CSX700 crystal contains 192 high-performance processor cores, built-in 256 KB buffer memory (two 128 KB banks), data and instruction cache, ECC protection of internal and external memory, built-in DMA controller. ClearConnect NoC technology is used to provide on-chip and inter-chip networks (Fig. 11).
The processor consists of two relatively independent MTAP modules (MultiThreaded Array Processor) containing instruction caches, data caches, control units for processing elements, and a set of 96 computational cores (Fig. 12).
Figure: 12. The structure of the MTAP block
Each core has a double block of floating point calculations (addition, multiplication, division, square root calculation, single and double precision numbers are supported), 6 KB of high-performance RAM, 128-byte register file. 64-bit virtual address space and 48-bit real are supported.
Specifications processor:
the clock frequency of the cores is 250 MHz;
96 GFlops for double or single precision data;
supports 75 GFlops in Double Precision Matrix Multiplication (DGEMM) test;
performance of integer operations 48 ShAOs;
power dissipation 9 W;
bandwidth of internal memory buses 192 GB / s;
two external memory buses 4 GB / s;
data exchange rate between individual processors 4 GB / s;
pCIe interfaces, 2 DDR2 DRAM (64 bit).
Designed for systems with low power consumption, this processor operates at a relatively low clock speed and has a frequency control mechanism that allows you to adjust the performance of applications under specific power and thermal environments.
CSX700 Supported professional environment Development Kit (SDK) based on Eclipse technology with visual debugging tools based on an optimized ANSI C compiler with extensions for parallel programming. In addition to the standard C library, there is a set of optimized libraries with functions such as FFT, BLAS, LAPACK, etc.
Modern Intel and AMD processors
The modern processor market is divided by two main competitors - Intel and AMD.
Intel processors are considered the most productive today, thanks to the Core i7 Extreme Edition family. Depending on the model, they can have up to 6 cores simultaneously, clock speeds up to 3300 MHz and up to 15 MB of L3 cache. The most popular cores in the desktop processor segment are based on Intel - Ivy Bridge and Sandy Bridge.
Intel processors use proprietary proprietary technologies to improve system efficiency.
1. Hyper Threading - Due to this technology, each physical core of the processor is capable of processing two threads of calculations simultaneously, it turns out that the number of logical cores actually doubles.
2. Turbo Boost - Allows the user to commit automatic overclocking processor, while not exceeding the maximum allowable operating temperature of the cores.
3. Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) - The QPI ring bus connects all processor components, thereby minimizing all possible delays in the exchange of information.
4. Visualization Technology - Hardware support for virtualization solutions.
5. Intel Execute Disable Bit - Practically antivirus program, it provides hardware protection against possible virus attacks based on buffer overflow technology.
6. Intel SpeedStep-Tool that allows you to change the voltage level and frequency depending on the load on the processor.
Core i7 - currently the company's top line
Core i5 - high performance
Core i3 - low price, high / medium performance
The fastest AMD processors are still slower than the fastest Intel processors (as of November 2010). But thanks to its good value for money, aMD processors, mainly for desktop PCs, are a great alternative to Intel processors.
For Athlon II and Phenom II processors, not only the clock speed is important, but also the number of processor cores. Athlon II and Phenom II, depending on the model, can have two, three or four cores. The six-core model is the Hig-end Phenom II series only.
Most modern AMD processors support the following technologies by default:
1. AMD Turbo CORE - This technology is designed to automatically adjust the performance of all processor cores through controlled overclocking (Intel has a similar technology called TurboBoost).
2. AVX (Advanced Vector Extensions), XOP and FMA4 - A tool that has an extended set of commands specifically designed for working with floating point numbers. An unambiguously useful toolkit.
3. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) - B software applications using data encryption improves performance.
4. AMD Visualization (AMD-V) - This virtualization technology helps to share the resources of one computer between several virtual machines.
5. AMD PowcrNow! - Power management technology. They help the user achieve better performance by dynamically activating and deactivating parts of the processor.
6. NX Bit - A unique anti-virus technology that helps prevent infection of a personal computer with certain types of malware.
Use in GIS
Geographic information systems are multifunctional tools for analyzing tabular, textual and cartographic data, demographic, statistical, land, municipal, address and other information. Lot nuclear processors necessary for fast processing different types information, since they significantly speed up and distribute the work of programs.
CONCLUSION
Moving to multi-core processors is becoming the main focus for improving performance. At the moment, the most common is considered to be 4- and 6-core processors. Each core is perceived by the system as a separate, independent processor, with all the necessary set of functions. The technology of multi-core processors made it possible to parallelize the computing operations, as a result of which the PC speed indicator increased.
http://www.intuit.ru/department/hardware/mcoreproc/15/
http://kit-e.ru/articles/build_in_systems/2010_2_92.php
http://softrew.ru/instructions/266-sovremennye-processory.html
http://it-notes.info/centralnyj-processor/
http://www.mediamarkt.ru/mp/article/AMD,847020.html
Benefits of multi-core processors
Ability to distribute the work of programs, for example, main tasks of applications and background tasks operating system, over several cores;
Increase the speed of programs;
Computationally intensive processes are much faster;
More efficient use of computationally demanding multimedia applications (for example, video editors);
Reduced energy consumption;
The work of the PC user becomes more comfortable;
Nowadays, the minimum acceptable standard for a more or less serious computing technology the presence of a dual-core processor is considered. Moreover, this parameter is relevant even for mobile computer devices, tablet PCs and solid smartphones-communicators. Therefore, we will figure out what kind of kernels are they and why it is important for any user to know about them.
The essence in simple words
The first dual-core chip designed specifically for mass consumption appeared in May 2005. The product was called Pentium D (formally it belonged to the Pentium 4 series). Before that, similar structural solutions were used on servers and for specific purposes, they were not inserted into personal computers.
In general, the processor itself (microprocessor, CPU, Central Processing Unit, central processing unit, CPU) is a crystal on which billions of microscopic transistors, resistors and conductors are applied using nanotechnology. Then gold contacts are deposited, the "pebble" is mounted in the microcircuit case, and then all this is integrated into the chipset.
Now imagine that two such crystals are installed inside the microcircuit. On a single substrate, interconnected and acting as a single device. This is the dual core topic of discussion.
Of course, two "pebbles" are not the limit. At the time of this writing, a PC equipped with a chip with four cores, not counting the processing resources of a video card, is considered powerful. Well, on servers, through the efforts of AMD, as many as sixteen are already used.
Nuances of terminology
Each die usually has its own L1 cache. However, if they have the same second level in common, then it is still one microprocessor, and not two (or more) independent ones.
A kernel can be called a full-fledged separate processor only if it has its own cache of both levels. But this is necessary only for use on very powerful servers and all kinds of supercomputers (favorite toys of scientists).
However, Windows' Task Manager or GNU / Linux 'System Monitor' can show kernels as CPUs. I mean, CPU 1 (CPU 1), CPU 2 (CPU 2), and so on. Do not let this mislead you, because the duty of the program is not to understand the engineering and architectural nuances, but only to interactively display the load of each of the crystals.
This means that we are smoothly moving on to this very load and, in general, to questions of the expediency of the phenomenon as such.
Why is it needed
The number of cores, different from one, is conceived primarily for the parallelization of tasks.
Suppose you turn on your laptop and read sites on the World Wide Web. Scripts, with which modern web pages are simply overloaded obscenely (except for mobile versions), will be processed by only one core. A hundred percent load will fall on him if something bad drives the browser crazy.
The second crystal will continue to work in normal mode and will allow you to cope with the situation - at least open the "System Monitor" (or terminal emulator) and forcibly terminate the frozen program.
By the way, it is in “ System Monitor"You will be able to see with your own eyes which software suddenly went off the rails and which of the" pebbles "makes the cooler howl desperately.
Some programs are initially optimized for multicore processor architecture and immediately send different data streams to different crystals. Well, ordinary applications are processed on the principle of "one thread - one core".
That is, the performance gain will become noticeable if more than one thread is active at the same time. Well, since almost all operating systems are multitasking, the positive effect of parallelization will appear almost constantly.
How to live with it
With regards to computing technology of mass consumption, chips with one core nowadays are mainly ARM processors in simple phones and miniature media players. Outstanding performance is not required from such devices. The maximum is to launch the Opera Mini browser, ICQ client, a simple game, and other unassuming applications in Java.
Everything else, starting even with the cheapest tablets, must have at least two crystals in the chip, as stated in the preamble. Buy such things. Proceeding at least from those considerations that almost all user software is rapidly gaining weight, consuming more and more system resources, so the power reserve will not hurt at all.
Previous publications:
What is the advantage of dual-core processors?
When buying a laptop, you probably noticed that some of them have labels: "Intel Core 2 Duo" or "AMD Turion 64 x2". These labels indicate that the notebooks are based on dual-core technology.
Dual core processors
Dual-core processors refer to a type of system that consists of two independent processor cores combined in a single integrated circuit (IC) or, as the professionals say, a single chip. Such systems combine two cores in one processor. A similar technology was first applied to personal computer and to the home game console, but very soon it was adapted to the mobile computer environment... AMD and Intel have laptops with similar technology.
Dual-core processors have a different structure than dual-core single-core processors. They refer to a system where two processors are combined in one integrated circuit. And dual single-core processors, in turn, refer to a system where two independent processors (each with its own matrix) are directly connected to the motherboard.
Each of the processors in a dual-core system has built-in cache memory (primary cache memory), which gives them their own potential to quickly and efficiently recover and process frequently used instructions. In addition, the same integrated circuit contains a L2 cache. The secondary cache on Intel's Mobile Core 2 Duo chipset is shared by two processors. In the Turion AMD 64x2 chipset, each of the two processors has a dedicated cache of 512KB per core. L2 cache is a reserve for in case the primary is not enough.
The advantages of dual-core technology
The most important advantages of such processors are speed and efficiency. Command processing and data retrieval are performed by two processors; thus, high performance is achieved without heating the processors. The fact that the two processors have their own readily available primary cache also ensures fast uptime. In addition, especially in the case of the Intel Core 2 Duo, where the secondary cache is split, all of the secondary cache can be used by either one or both processors at the same time, if the need arises.
In a nutshell, a laptop with a dual-core processor runs faster and heats up less, while also offering improved multitasking. Dual-core processors consume less power than dual-core processors.
Another advantage of using dual-core processors in laptops is the lighter weight and size, which makes portable PC more convenient while delivering PC-like performance.
It is important to note that with older programs, if you only run one program at a time, you will not experience any of the benefits of dual-core processors. Older programs were not designed for this technology, so they can only use one core. However, in this case, the advantage of multitasking still remains. If you open multiple programs at the same time, then a dual-core processor will provide faster performance than a single-core processor.
As time goes on, more and more software developers are creating their programs with dual-core processors in mind; thus, users in the near future will be able to experience all the benefits of such processors.
The core is a crystal (stone), a silicon chip, which is the processor itself.
The kernel is like a version (variant) of the processor.
Processors with different cores, you can say different processors.
Different cores differ in cache size, bus frequency, manufacturing technology, etc.
The newer the core, the better processor accelerates.
An example is P4, which has (at the moment) two Willamette and Northwood cores.
The first core was produced using 0.18 micron technology and worked exclusively on the 400 Mhz bus.
The youngest models were clocked at 1.3 Ghz, the maximum core frequencies were slightly above 2 Ghz.
These processors were not particularly famous for their overclocking qualities.
Northwood was later released.
It was already made using 0.13 micron technology and supported the bus in 400 and 533 Mhz, and also had an increased cache memory.
The transition to a new core allowed a significant increase in performance and maximum frequency.
Younger Northwood processors with 1.6 Ghz overclock perfectly.
Of this example you can conclude for yourself that these are different processors.
Within the same architecture, different processors can be quite different from each other.
And these differences are embodied in a variety of processor cores that have a certain set of strictly determined characteristics.
Most often, these differences are embodied in different system bus (FSB) frequencies, L2 cache sizes, support for certain new instruction systems or technological processes by which processors are manufactured.
Often, changing the core in the same processor family entails replacing the processor socket, which leads to further compatibility issues motherboards.
In the process of improving the kernel, manufacturers have to make minor changes to it, which cannot pretend to be a "proper name".
These changes are called kernel revisions and are most often denoted by alphanumeric combinations.
However, in new revisions of the same kernel, there may be quite noticeable innovations.
For example, Intel introduced support for the 64-bit EM64T architecture into individual Pentium 4 processors precisely during the revision change process.
Answers on questions
Radeon Software Adrenalin Edition 17.12.1 - New AMD Driver Package
New drivers bring performance improvements in many popular gameswhich include Tom Clancy's Ghost Recon Wildlands, Mass Effect: Andromeda Overwatch, Prey and Project Cars 2.
Compared to the Radeon Software Crimson ReLive Edition drivers, owners of Radeon adapters can expect 10-19% performance gains.
True, here it is necessary to make a reservation that the performance of Adrenalin is compared with the very first version of ReLive drivers.
In addition, developers have reduced response times - in projects like Counter Strike, every millisecond counts.
Holders of configurations with two video cards running in crossFire modewill appreciate the performance gain.
For example, in Far Cry Primal, a pair of Radeon RX 580 is exactly twice as fast as one video card.
Radeon WattMan technology has been enhanced to allow custom profiles to be saved, reloaded at a later time, and transferred to other Radeon users.
Cryptocurrency miners are not forgotten either.
When using a special computing mode (Compute Profile), the increase reaches 15% - such results were obtained on a system with a Radeon RX 570 4GB video card when mining Ethereum cryptocurrency.
The technology called Radeon Chill has been improved and now works in almost all games.
Let us briefly recall its essence: when you slow down the movement in the game, the frame rate decreases.
Reducing performance also reduces energy consumption.
This saves battery life in the laptop.
A pleasant side effect of this technology is noise reduction.
Not forgotten is the emerging phenomenon of video game streaming.
New software AMD has a very wide range of possibilities for organizing high-quality streaming of games on the Internet.
Directly through the driver control panel, you can link your YouTube or Twitch accounts to easily organize live streaming of games to the global network.
Intel unveils Gemini Lake generation processors
It is a very low power consumption CPU targeted at compact PCs, relatively budget models, hybrid solutions and various devices, where the TDP level is critical.
Gemini Lake processors have replaced the Apollo Lake generation, which has filled the niche of cheap laptops due to the almost complete absence of budget CPUs of the older Intel families.
Gemini Lake is a follower of the Atom family, it's just that Intel doesn't use this brand right now.
In total, there are six processors in the new generation: a pair of Pentium Silver and four Celeron models.
At the same time, three models conditionally refer to the desktop segment, and three - to the mobile one.
Models with the N index belong to the mobile segment, and those with the J index - to the desktop segment.
All processors received a dual-channel memory controller with DDR4 / LPDDR4 support.
GPU UHD Graphics 600 contains 12 execution units, while UHD Graphics 605 has 18 units.
The CPUs are manufactured using a 14-nanometer process technology and have the FCBGA1090 performance regardless of the platform.
Local Adaptive Contrast Enhancement (LACE) technology debuts in processors.
Judging by the description, it is designed to adjust the image on the screen depending on the ambient light.
In addition, Intel claims that Gemini Lake processors were the first among the company's solutions to receive support for Gigabit Wi-Fi.
More precisely, it uses the 2 × 2 802.11ac standard with 160 MHz channels.
It can also be noted support for HDMI 2.0 and image output in 4K at 60 fps.
The first PCs based on the new CPUs will appear in the first quarter of 2018.
About 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen Processors
AMD plans to release successors to the Ryzen desktop processors for the foreseeable future.
According to the leaked roadmap, the second generation Ryzen chips, also known as Pinnacle Ridge, will debut at the end of February.
The new processors are reportedly to be manufactured according to 12nm FinFET specifications at GlobalFoundries' facilities.
The older Ryzen 7 chips will be the first to hit store shelves, and then in March AMD will release more affordable solutions for the Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 3 lines.
These "stones" will receive the AM4 design and will be compatible with commercially available motherboards based on AMD 300 series chipsets.
It should be borne in mind that new motherboards based on AMD 400-series logic will be on sale with the mentioned CPUs, which are relevant for those who build a system from scratch or migrate from older platforms.
12-core solutions operating at significantly higher frequencies than their predecessors can lead the line of desktop processors for the AM4 platform.
In particular, the flagship Ryzen 7 2800X will be clocked at 4.6 to 5.1 GHz in boost mode, while the Ryzen 7 1800X will be clocked at 3.6 to 4 GHz.
Importantly, an increase in the number of cores will not in any way affect the recommended cost of new CPUs, which will be identical to the 8-core analogs already available on the market.
In fact, in every industry there is a division of products into target categories. There are tons of cheap products with basic features and functionality; they are intended for the vast majority of users. A small group of experts and professional users are targeted at expensive devices with a mass fine tuning and specific functions. And the gap between these two groups of users is not as small as it might seem at first glance.
It includes those people who no longer have enough entry-level opportunities; these users, so to speak, "grew", and budget products no longer satisfy them. On the other hand, top-end products are quite expensive for them, and in terms of experience, they have not yet "matured" to it. And it is for this group of people that companies release various mid-level products with an intermediate set of functions. And it does not matter at all what kind of products we are talking about, be it cell phones or cameras (which are almost the same now), stereos or cars.
Finishing this thought, we want to emphasize that many novice users often buy mid-level products "for growth." In other words, at the initial stage, they use only basic capabilities, but with the growth of experience, they gradually use more and more range of functions. Marketers are extremely successful in exploiting this idea, and in some industries, mid-priced products have the highest percentage.
Now let's turn directly to the subject of our review, namely, to the quad-core Intel Q8300 processor based on the Yorkfield core. Initially, all four-core processors were designed exclusively for workstations that are run by professional users. The latter use software packages corresponding to their level, which have optimization of multithreaded computations. For such users, our recommendations have always remained unchanged: to achieve the highest performance, you must purchase the latest platform (the exception was with NetBurst) and use the fastest processor, as well as the maximum possible (corresponding to the OS capabilities) amount of RAM.
However, besides professionals, there are many other users who sometimes work with multi-threaded programs. Someone is studying a new package in the evenings, someone is doing a "shabbat", and someone is developing blanks at home in order to finish them at work the next day. These are the users who need an inexpensive processor with the maximum number of cores.
Another group of users is completely far from multithreading and computers in general. They buy quad-core processors because they are "twice as good as dual-core."
The situation, in general, is not new - at one time it was "bought by megahertz". It is clear that these buyers do not get the real benefit from four cores, since the vast majority of home applications are not optimized for multithreading. Judge for yourself: after launching the game, you are forced to watch from one to four videos with the logos of the development companies and license holders. Another video can be introductory. And after the completion of all the videos, the game just starting to load, and does it long enough. Why can't the game load in parallel while scrolling videos? In principle, the answer is clear: it is much easier to develop programs without optimization, and most importantly, it is financially more profitable!
Well, okay, we have said all this more than once in one form or another. Now let's turn to Intel, which, after switching to a 45-nm process technology, quickly saturated the market with quad-core processors. top level... After that, Intel began to gradually introduce cheaper quad-core processors to the market, with a slightly reduced cache and relatively low clock frequencies.
The first such product was the Q8200 processor based on the Yorkfield core, with clock frequency 2.33 GHz and 1333 MHz QPB bus. Recall that most of the top-end 4-core processors of the Q9xxx series have L2 \u003d 12 MB (2x 6 MB) cache, and only the Q9300 model is equipped with L2 \u003d 6 MB (2x 3 MB). And so that cheaper processors do not overtake more expensive ones in speed, Intel continued the practice of "cutting" the L2 cache, and for the Q8xxx series its size was set at 4 MB (2x 2MB). Accordingly, the "table of ranks" for 4-core Intel processors is as follows:
| Name | Number of Cores |
Frequency, GHz |
Factor |
|||
| Core 2 Extreme QX9770 | ||||||
| Core 2 Extreme QX9650 | ||||||
| Core 2 Quad Q9550 | ||||||
| Core 2 Quad Q9450 | ||||||
| Core 2 Quad Q9300 | ||||||
| Core 2 Quad Q8300 | ||||||
| Core 2 Quad Q8200 |
In addition to these specifications, processors have one more parameter that is constantly changing (before the crisis, we would have written - decreasing). This is the retail price. For professionals, it does not play a role, but for semi-professional users it still plays. So for the latter, there is good news: the Q8300 test processor costs about $ 230, and its OEM version costs about $ 200! And, roughly speaking, we get four 2.5 GHz processors for $ 50 each. From the point of view of professionals, this is a freebie.
So, the freebie looks like this:
Back side:

The CPU-Z utility provides the following information:
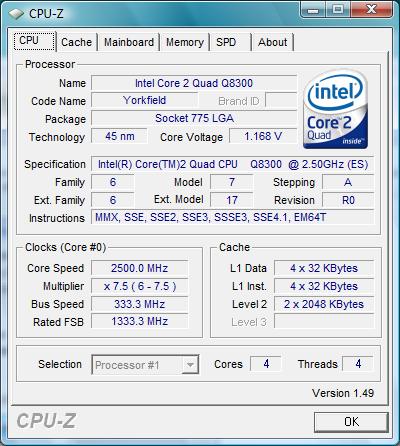
Functionally, this processor is in no way inferior to its older brothers. That is, the processor supports all extended instruction sets, as well as all modern Intel technologies in terms of energy efficiency. The only thing that distinguishes the "eighth" series from the "ninth" is the absence of virtualization technology.
Overclocking
A few words about overclocking. On the one hand, the Q8300 should be very attractive in terms of overclocking. This assumption is supported by the fact that the frequency potential of the Yorkfield core is in the 4 GHz region. Moreover, we reached this frequency even more than a year ago, when we tested the Core 2 Extreme QX9650 processor. Since then, Intel has certainly optimized and refined the process, and the frequency potential has increased.
However, there are some negative points to consider. First, we overclocked the QX9650 by increasing the multiplier, which is unlocked for this model. On the contrary, the Q8300 has a locked multiplier, and a relatively high FSB frequency means a rather low nominal multiplier. He, in fact, is so, and is equal to 7.5; besides, it is also blocked.
As a result, to overclock up to 4 GHz, the FSB frequency should be around 533 MHz. For most modern motherboards, this frequency is not something transcendental: we constantly reach frequencies of 550 MHz and higher. However, it should be borne in mind that these tests are carried out with a dual-core processor, while a processor with four cores significantly increases the load on the system bus. As a result, the overclocker is forced to significantly increase the FSB voltage, raise the PLL voltage, and pick up the GTL. Still, most enthusiasts face significant challenges around 500 MHz. We also faced these problems: the final result was a stable FSB frequency of 480 MHz, which gave a resulting processor frequency of 3.6 GHz.
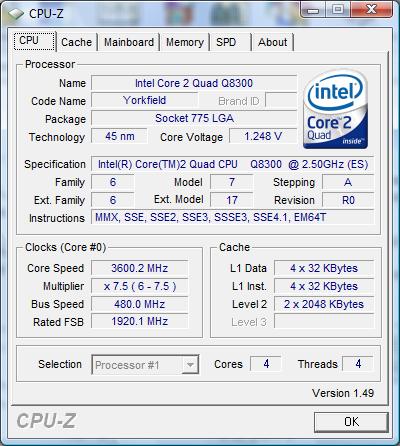
On the one hand, the result can be considered quite good, since Intel uses the "best cores" for the production of expensive high-frequency processors, and what remains for the cheap ones. On the other hand, we were left with the strong impression that if the multiplier had been unlocked, we would have safely run the Q8300 at 4 GHz.
Performance
The following equipment was used in the test system:
| Test Equipment | |
| Motherboard | ASUS P5E3 Premium on Intel X48 |
| Cooler | Gigabyte g-power |
| Video card | ASUS 8800 GT (GeForce 8800 GT; PCI Express x16)
Driver version: 180.48 WHQL |
| Sound card | - |
| HDD | Samsung HD160JJ |
| Memory | 2x1024 MB Qimonda DDR3-1333; |
| Housing | FSP 550W |
| OS | MS Vista |
First, let's look at the results of synthetic tests.




Application software tests.


Video encoding (DivX, Xvid) was measured in seconds, i.e. less is better.


Data compression (WinRAR) was measured in kbps, i.e. more is better.

Now - tests of game programs.







conclusions
From a performance standpoint, the Q8300 is exactly where Intel marketers took it. That is, it is faster and more expensive than the Q8200 processor, but slower and cheaper than the others. quad core processors Intel. And a few months ago, the conclusion would have sounded like this: when choosing a 4-core processor, you need to pay attention to Intel products and be guided by your financial capabilities.
However, with the release of the new AMD Phenom II processors, the situation has become somewhat complicated, since the choice has become larger, and it has become more difficult to solve the problem of choosing a processor. The point is that the specific performance of AM3 processors is practically the same as that of Intel processors. And yet AMD processors are cheaper. Specifically, the Phenom II X4 805 retails for around $ 210 (March 2009). Accordingly, our advice to those users who are starting to work with professional software packages is as follows.
At the first stage, it is necessary to assess the degree of optimization of the software used for multithreaded computing. If such optimization is present, then it makes sense to switch to 4-core processors. Then you need to determine for which processors the software used is optimized, and on the basis of this, purchase a processor from the right manufacturer. And only after that it makes sense to choose a specific processor model based on the cost.
For those users who are planning to overclock their processor, we want to remind you once again that the Q8xxx series processors have relatively low locked multipliers, and in most cases you will not be able to reach the technological limit of the Yorkfield core.
By the way, if overclocking in professional workstations is unambiguous (because 100% stability is important there), then for a home system it is only welcome. The fact is that without significant financial costs, you can significantly increase productivity. At the same time, the loss of data or calculation results will not cause significant harm, since your semi-professional work is a kind of hobby.
