So you've got a brand new SSD. You installed the system on it, armed yourself with the optimization guide found on the net and after a couple of hours did everything possible to ... slow down your work in the system!
Don't believe me? Think about what makes high performance. Benefits sSD speed you can experience in three categories:
- system, for example, the speed of its loading and operation
- programs, including web surfing and working with documents, images and media files
- your actionsincluding navigating the disk and copying / moving files
How myths are born
I'm pretty sure your SSD tweaking steps have negatively affected at least one of these components. Below you will find out why this happened, but first about the reasons for this optimization.
If you read the inscription "buffalo" on an elephant's cage ...
 There are tons of guides and even tweakers online for optimizing your SSD. In fact, the same information is used everywhere, and:
There are tons of guides and even tweakers online for optimizing your SSD. In fact, the same information is used everywhere, and:
- outdatedbecause it aims to save disk space and reduce the number of rewriting cycles, which is irrelevant for modern SSDs in home PCs
- uselessbecause Windows itself takes care of what they suggest to configure
- harmful, because it leads to a decrease in the speed of work - yours, programs and system
Take a look critical to your guide or tweaker and consider which items fall into one of these categories!
There is one more problem - unsuccessful presentation of information, including incorrectly placed accents.
If you have an HDD along with an SSD, measure the speeds of both drives and keep the picture in mind. I will return to her, and more than once!
Special notes for dissent
After the publication of the material, I decided to specifically clarify a few points, so as not to repeat them regularly in the comments, answering opponents.
In this article:
- All myths are considered solely from the point of view of speeding up the system, programs and users.... If a measure is declared useless or harmful, this means that it does nothing to speed up work.
- Reducing the amount of writing to disk is not considered an optimization measure due to the irrelevance of this approach. If that's your goal, myths 3-11 are for you, as is storing an SSD in a sideboard.
- RAM disk usage is not considered as it is not directly related to SSD optimization... If you have an excess of RAM, you can use a RAM disk regardless of the type of drives installed in your PC.
- All recommendations are made taking into account a wide audience, i.e. the majority users... When analyzing tips, keep in mind that they may not correspond to your tasks, work skills and ideas about optimal and competent use. operating system.
Now let's go! :)
Myths
1. Disable SuperFetch, ReadyBoot and Prefetch
This tip: controversial, may slow down programs launching
At launch of each program, the prefetcher checks for a trace (.pf file). If found, the prefetcher uses MFT metadata links file system to open all required files... Then it calls a special function of the memory manager to asynchronously read data and code from the trace that are not currently in memory. When the program is launched for the first time or the startup script has changed, the prefetcher writes a new trace file (highlighted in the figure).
SuperFetch is unlikely to be able to speed up the launch of programs from an SSD, but Microsoft does not disable the feature, given the presence of hard drives in the system. If a proprietary utility from the SSD manufacturer (such as Intel SSD Toolbox) recommends disabling SuperFetch, follow its advice. However, in this case, it is more than logical to keep all programs on the SSD, which will be discussed below.
2. Disable Windows Defragmenter
This tip: useless or harmful, can degrade disk performance
One of the functions of the CheckBootSpeed \u200b\u200butility is to check the status of the Defragmentation Scheduled Job and the Task Scheduler service. Let's see how relevant these options are for the latest Microsoft operating systems installed on SSDs.
Windows 7
Windows 7 does not defragment SSDs, which is confirmed by the words of the developers in the blog.
Windows 7 will disable defragmentation for SSD drives. Since SSDs perform excellently on random reads, defragmentation will not provide the same benefits as on a regular disk.
If you don't believe the developers, take a look at the event log. You will not find records of defragmentation of the SSD volume there.
Thus, when the SSD is the only drive, the scheduled task simply does not run. And when the PC also has an HDD, disabling the task or the scheduler deprives hDD worthy of optimization with a regular defragmenter.
Windows 8 and newer
In Windows 8, the Disk Optimizer has replaced the defragmenter!
Optimizing hard drives, as before, comes down to defragmentation. Windows no longer ignores solid-state drives, but helps them by sending to the controller additional a set of TRIM commands at once for the entire volume. This happens on a schedule as part of automatic maintenance, i.e. when you are not working on a PC.
Depending on the SSD controller, garbage collection can be performed immediately upon receipt of the TRIM command, or delayed until a period of inactivity. Disabling Disk Optimizer or Job Scheduler degrades drive performance.
3. Disable or move the paging file
This tip: useless or harmful, slows down the system speed when there is insufficient memory
The hardware configuration must be balanced. If you have little memory installed, you should add it first, because it is cheaper and provides a more tangible performance boost than buying an SSD.

When you have enough memory, the paging file is hardly used, i.e. this will not affect the life of the disk. But many people still turn off the pumping - they say, let the system keep everything in memory, I said! As a result, Windows Memory Manager does not run at its best (see # 4).
As a last resort, the paging file is transferred to the hard drive. But if suddenly there is not enough memory, you will only benefit in performance with pagefile.sys on the SSD!
IN: Do I need to place the paging file on the SSD?
ABOUT: Yes. The main operations with the paging file are random writes of small amounts or sequential writes of large amounts of data. Both types of operations perform well on an SSD.
By analyzing telemetry focused on evaluating swap file writes and reads, we found that:
- reading from Pagefile.sys prevails over writing to pagefile.sys in a combination of 40: 1,
- read units for Pagefile.sys are usually quite small, 67% are less than or equal to 4KB and 88% are less than 16KB,
- the write blocks in Pagefile.sys are quite large, 62% of them are greater than or equal to 128 KB and 45% are almost exactly 1 MB
Generally speaking, the typical paging file usage patterns and SSD performance characteristics fit together perfectly, and it is this file that is highly recommended to be placed on an SSD.
But in practice, the desire to extend the life of an SSD at any cost is ineradicable. Here is a blog reader shaking over his SSD, transferring pagefile.sys to the hard drive, although he himself can even see with the naked eye that this decreases performance. By the way, I can't install more than 2 GB of memory in my netbook, and it became much more comfortable with a solid-state drive than with a standard HDD 5400 rpm.
Finally, remember that completely disabling the paging file will prevent you from diagnosing critical errors. The paging file size is flexible, so you always have a choice between disk space and performance.
Tricky question: What was my paging file size when I took a screenshot of the Task Manager?
Special note
On the Internet (including in the comments to this post), you can often find the statement: “The paging file is not needed if you have installed NGB RAM ". Depending on the fantasy N takes the value 8, 16, or 32. This statement does not make sense because it does not take into account the tasks that are solved on a PC with a given amount of memory.
If you have installed 32GB for yourself, and you are using 4-8GB, then yes, you do not need an FP (but then it is not clear why you bought 32GB RAM :). If you have acquired enough memory to use it as much as possible in your tasks, then FP will come in handy.
4. Disable hibernation
This tip: inaudible and harmful to mobile PCs, may decrease battery life and speed.
I would formulate the advice like this:
- stationary PCs - shutdown is normal. you can use sleep as well
- mobile PCs - turning off is not always advisable, especially with high battery consumption during sleep
However, people have turned off, turn off and will turn off system protection regardless of the type of disk, this is already in the blood! And no, I don't want to discuss this topic in the comments for the hundredth time :)
6. Disable Windows Search and / or Disk Indexing
This tip: useless, reduces the speed of your work
Sometimes this is argued that SSDs are so fast that the index will not significantly speed up searches. These people just never really used Windows Search!
I find it pointless to deprive yourself of a useful tool to speed up everyday tasks.
If you fall victim to any of these myths, tell us in the comments if I managed to convince you of their uselessness or harm and in what cases. If you disagree with my assessment of "optimization", explain what the benefits of these actions are.
Configuring SSD for Windows 7
Introduction
Solid state drives are said to be significantly faster than mechanically based hard drives. Of course, their cost is much more expensive. Although SSD performance figures are high, many users claim that they can be improved. All that is required is the appropriate optimization and tuning of the SSD for Windows 7. The most effective methods in this article will be considered:
- Enabling AHCI and TRIM
- Disabling system protection
- Disconnection
- Disable hibernation
- Disable Windows 7 Write Caching
- Disabling Super fetch and Windows 7 search
- Power Options Settings
Enabling AHCI and TRIM
Before starting the optimization, you need to make sure that the SATA controller can work in AHCI mode and the TRIM function in Windows 7 is activated.
During system startup, press the DELETE key and see that the BIOS has enabled AHCI mode for your SATA controller. This mode is required to support TRIMa on SSDs. You can also verify this by performing the following actions in the system:
- In the start menu "Start" select "Control Panel"
- Select "System" and switch to classic view (small and large icons mode)
- Go to " "
- Look for an item with a list of ATA / ATAPI and IDE controllers
- If there is such an item, your system is already loaded with the AHCI mode enabled

If the operating system was installed with IDE mode, then you need to switch to AHCI mode in the BIOS, provided that the motherboard supports this functionality.
- Check that TRIM support is activated
- Check TRIM so that mode commands are guaranteed to be sent by the Windows 7 operating system to the SSD drive.
- In the start menu, type [cmd] on your keyboard to find the command line built into the system
- Push it down right key mouse, choosing "Run as administrator"
- On the command line, write [fsutil behavior query Disable Delete Notify]
If the Disable Delete Notify parameter is 0, the TRIM function is activated. If the value is 1, it is disabled.

Do not use parentheses when entering a command.
The SATA-TRIM protocol command will tell the OS which blocks of the data previously written to the SSD will never be required in the future due to deleting files or formatting the disk.
Disabling system protection


Disable System Protection to limit the number of writes to SSD diskx, as well as to return the vacated, due to disconnection, place back to solid state drive.
Disable disk indexing
Description of the deactivation process:

It is possible that a pop-up window will appear informing you of an error in applying attributes to files, which is normal. Continue with the "Ignore All" option.

The meaning of disabling disk indexing boils down to the following:
- Disk indexing was designed for mechanical devices to provide quick access to information. Considering that the response time of an SSD drive is approximately 0.1ms, there is no need to enable this technology.
- By eliminating unnecessary read / write operations on the SSD, we get minimal effect. However, keep in mind that actions to limit the number of write cycles to an SSD will help extend the lifespan of your SSD.
Disable paging file
- Right-click on the "My Computer" icon
- Select the item "Properties"
- Select the "Advanced" tab
- In the "Performance" item, click on the "Options" button
- Select the "Advanced" tab and click on the "Change for virtual memory" button
- Remove the "Automatically select paging file size" checkbox
- Agree to accept the changes, confirming the system reboot, and the next step is to disable swapping for your SSD.
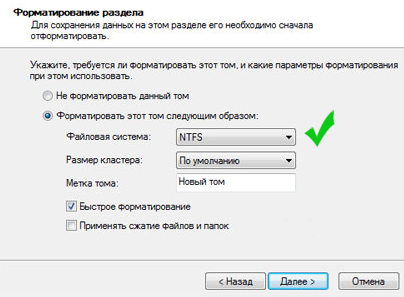
A paging file is a Windows functionality that is designed to help the computer's physical memory in case of insufficient capacity, allowing the transfer of some information from the "RAM" to the hard disk to free up the available RAM. Turning off the PageFile function will free up paging space on your hard drive.
Disable hibernation
Disabling hibernation mode will free up 2 Gb (possibly more, depending on the amount of RAM installed) of the SSD disk space. This functionality will not provide significant benefits due to fast loading.
Description of the deactivation process:
- In the Start Search menu, type [cmd] to search windows utilities 7
- Right-click on the cmd program and run it as administrator
- Type [powercfg -h off] at the command line

Hibernation helps the system recover quickly from inactivity. When it is applied, the information contained in the random access memory device is written to disk, and then read out upon waking up.
Disable Windows Write Caching
Description of the deactivation process:
- Press the right mouse button on the "My Computer" icon, choosing "Properties"
- Select "Device Manager"
- Select "Disk drives"
- Press the right mouse button on the SSD by selecting Properties
- On the "Politician" tab, remove the "checkbox" from the item "Allow to cache records on this device"

The write caching functionality in Windows 7 can access high-speed RAM and accumulate commands that then need to be executed on SSD storage... SSD drives outperform mechanical drives hard disks, therefore, there is no gain in speed when using the cache.
Disable Superfetch and Windows Search
Description of the deactivation process:
- Press Windows Key + R to enter the application launcher dialog.
- Type in and press the Enter button.
- Scrolling down the "scrollbar" to the item "Superfetch", right-click on it, choosing "Properties"
- From the Startup Type dropdown menu, selecting Disabled, click OK.
- Scrolling the "scrollbar" to the item "Windows Search", right-click on it, selecting "Properties"
- Click on the "Stop" button, then on "Startup type" and select "Disabled".

Function Windows Search creates an index of some folders, files and additional objects on your devices. He is in the Program folder Data Microsoft Search on the TRIMa: / drive and occupies about 10% of the content of the indexed information. When searching for a file, parts of the indexes are loaded into memory. This will provide a reasonably fast search. This functionality will not matter much, and can also negatively affect the performance of an SSD drive.
Disable Clear Page File At Shutdown and Large System Cache
Description of the deactivation process:
- Type in the start menu
- Select the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SYSTEM Current Control Set Control Session Manager Memory Management
- Click the right mouse button on "Clear Page File At Shutdown" and "Large System Cache"
- By choosing Change, change the value from 1 to 0, and then restart the system.

This OS functionality is designed to clear the paging file. This leads to an increase in the number of read-write operations. Since the paging file was previously disabled, there is no longer any reason to use cleanup, as there is nothing to clean up.
The Large System Cache parameter indicates whether the operating system supports a standard cache size or an increased one, and is also responsible for the frequency of processing cached data. Enabling Large System Cache mode will reduce the amount of physical memory available to applications and services.
Setting energy options:
- Open your "Control Panel"
- Select "System and Security" in it
- Select Power Settings
- Select the "High performance" checkbox and apply it with the OK key
- Select "Power plan settings" for your "High performance" plan
- Click on the item to change advanced power settings
- In the item "Hard disk" set in the drop-down menu to disable hard disk "Never" mode
- Click OK to save the setting.

Conclusion
Setting up an SSD for Windows 7 can affect system performance, both positively and negatively. Suppose there is no need to enable write caching when using the Intel X25M / G2, since in this case, as is usually the case, you cannot achieve it. So is it worth performing the actions discussed in the article at all?
One important factor in SSD optimization is the increase in storage capacity.
This will give undeniable advantageif an operating system is installed on the SSD windows system 7. It becomes possible to install more software, games and other software. Disabling System Protection, Disk Indexing, Paging File, and Hibernation will slightly improve performance, but the free capacity of the SSD will increase significantly.
The most discussed issue among SSD users is disconnecting, moving or saving the paging file. There is no single opinion and there are many supporters of various options. If you plan to disable the paging file, then you need to check the amount of memory used by Windows 7. Make sure the volume installed memory half more than the maximum used. In this case, the paging file can be disabled without losing PC performance. Alternatively, its size can be reduced or moved altogether.
Disabling unnecessary operations when reading and writing data to an SSD disk effectively affects the life of the device. Considering the cost of solid state drives, this is an important advantage.
As a result, the user decides for himself whether he needs to configure the SSD under Windows 7 or not. This OS from Microsoft already works quite well with SSDs, but with the additional optimization steps taken, there is the possibility of a small gain in performance compared to working with the "default" settings.
we have already told you what an SSD is and how to install it correctly in a laptop or computer.
But in addition to all of the above, it is necessary to clarify one more point: Windows 7 itself is not very optimized for working with SSDs.
It was developed and created to work with conventional mechanical HDD. And some of the services and operations that Windows 7 produces not only do not speed up the system, but in addition also leads to incomprehensible "glitches" when working with the SSD and to its rapid wear.
In this article, we'll show you how to properly configure and optimize Windows 7 for SSD use.
Before working with an SSD highly recommended update the SSD firmware from the manufacturer's official website. In order to subsequently avoid "glitches" in the work.
Now almost all SSDs can be updated directly from under Windows, along with data. But for safety reasons, it is better to do this on a "clean SSD", in order to avoid the loss of important information.
For instructions and methods for flashing your SSD, look for only on the official websites and forums of manufacturers.
So. After installation required drivers, we need to optimize the OS itself.
More specifically:
- Disable or transfer the OS swap file;
- Disable indexing and SSD caching;
- Disable SSD defragmentation;
- Disable Prefetch and Superfetch;
- Disable system restore;
- Disable Hibernation;
- Check if TRIM is enabled
- In SSD + HDD systems, you can transfer the TEMP folder.
Note: all these manipulations are not a panacea, and no one will give you a 100% guarantee. There have been cases where disabling caching reduced the performance of some SSDs (mainly on the SandForce controller).
As a result, everyone decides for himself whether this optimization is needed for his SSD.
And so, if you still firmly decided that you need optimization, then let's proceed to the settings:
First thing disable or transfer the swap file.
It is used by the system to store temporary data when there is a lack of RAM.
Frequent access, or rather writing / rewriting data on an SSD, quickly wears out its cells.
So it will be optimal disable swap file
if you have the amount of RAM more 4Gb
.
If 4Gb or less, then it should be transferred to the HDD or increase the amount of RAM.
To disable the paging file you need on the icon A computer right-click and enter Properties systems

Then in the tab Extra options systems / Advanced / Options / Advanced click Edit

Uncheck "automatically" and put "no swap file" and click Ask

The system will swear, but we agree and then restart the computer.
If there is not enough RAM, then we can transfer the paging file, indicating which disk to reserve space on or set the minimum size that the system will ask for.

Also in systems where SSD and HDD are installed, you can transfer from SSD to HDD system folder TEMP, in which Windows stores temporary files.
- create a TEMP folder on the HDD, for example, on the D drive (provided that D: is a partition on the HDD), and make it hidden so that the eyes are not "callous" :)
- Right-click on the "Computer" icon and select "Properties".
- In the window that opens on the left, select the item "Additional system parameters".
- On the Advanced tab, click the "Environment Variables" button

Change the value "TEMP" and "TMP" to D: \\ TEMP

Click "OK", then "Apply"
The next step disable indexing and SSD caching.
Since SSDs are much faster than HDDs and file search speeds and write speeds are much faster, these SSD features are unnecessary. In addition, we will improve the reliability of data recording during power outages. Disable these features so that data is not indexed in RAM and cached in the SSD buffer.
Note: for some SSD models based on the SandForce controller, it is not recommended to disable caching, as the read / write speed of the SSD may noticeably decrease (as well as the performance rating of the Windows 7 disk system).
In the explorer, right-click on the C: drive and in the C: drive properties, uncheck the "Allow indexing ..."
Apply to C drive only:


Right-click on our SSD and in the section Properties / Policy disable file caching

The next step disable SSD defragmentation.
On an SSD, direct access to files is already very fast and you don't need to defragment it.
This technology was developed for conventional HDDs and in the case of SSDs, it only harms the SSD cells.
Disable defragmentation in the properties of our C: drive. Right-click on the C: drive and on the tab Properties / Service / Defragment turn off Defragmentation on a schedule
![]()
You can also disable the defragmentation service under Management / Services , but if the system has SSD + HDD installed, then defragmentation for our regular HDD will not be available. The service can be completely stopped only on systems where only an SSD is used (for example, a laptop).


Next, disable Prefetch and Superfetch.
These are OS components that speed up the process bootstrap, as well as reducing the launch time of programs.
But since the SSD is already "smart", and the OS is loaded from it in a matter of seconds, we do not need them.
Prefetcher (prefetch) is a component of the Windows 7 memory manager, responsible for optimal loading of the operating system and frequently used programs. Prefetching is the selection and loading into RAM of the data needed to run certain processes before those processes are started. This technology, when using an SSD, it only clogs the RAM with unnecessary processes.
Superfetch performs all the functions of prefetching, plus a few additional functions. The advantage of superfetching is that it lacks one of the biggest drawbacks of Prefetching. Prefetching loads most of the files and data required to start an application or process into memory to speed it up. But when other applications access memory, the pre-selected data is swapped out to the hard drive, into the paging file. And when this data is required again, the system will load it back from the paging file into memory, which is not desirable, in order to avoid frequent overwriting of SSD cells.
You can disable these components in the Windows registry. To open the registry, simultaneously press the Win + R buttons (button Win  ) a window should appear Execute ...
) a window should appear Execute ...
And enter the command Regedit

Will open windows registry... We're crossing the path HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \\ SYSTEM \\ CurrentControlSet \\ Control \\ Session Manager \\ Memory Management \\ PrefetchParameters and in the parameters (double click on the parameter) EnablePrefetcher and EnableSuperfetch change the values \u200b\u200bto zero "0". Save changes

We also disable System Restore.
Although this is a moot point, it is necessary or not. But we will disable it to restrict writing information to our SSD.
For me, personally, it is better to restore the system from an Acronis True Image backup image than to search for system failure checkpoints.
You can disable recovery in Computer Properties / System Protection / Configure
Windows 7 and SSDs: Are Solid State Drives Faster?
Do solid state drives increase speed windows work 7? In short, the answer is unequivocal, yes. Conventional hard drives are usually the bottleneck in absolutely any computing environment. If you improve disk performance, such as read speed, the system boots up faster and the system starts up much faster.
From the data it can be seen that when using an SSD, the desktop loads faster by 62%, thereby reducing the total boot time of Windows to 54% (this number includes loading drivers, as well as processors with low priority, as well as third-party programswhich are added to startup).
My personal impressions also confirm the test results. If you use solid state drive, then the loading time can be reduced several times, and therefore applications will start at a very high speed - in just a second or even less.
1. Update BIOS to the latest firmware.
2. Upgrade the SSD Disk to the latest firmware (all data will be lost)
3. Place the disk controller in AHCI mode. Before installing a new operating system, bIOS settings you must activate AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) for the SATA controller. If you use legacy IDE or ATA modes, it will interfere with the installation of the driver for the disk controller and thereby reduce performance.
Advanced - SATA Configuration - Sata mode selection - AHCI
4. Secure Erase - erase the disk.
In order to perform a complete disk erase, use the Secure Erase utility. If you have been using the disc for long enough this can be incredibly useful, but it is not required. Do not format the drive using the built-in windows tools... For Intel drives, you can use the Intel Solid State Drive Toolbox. Lenovo computers have a disk cleanup function as part of the BIOS Menu Setup Extension utility. For OCZ drives, the Secure Erase utility can be downloaded from the OCZ Forum. Alternatively, you can use the HDDErase utility, which supports a wide variety of solid state drives.
5. Boot the system using the installation windows disk and run a clean installation. Use Windows Installer to create partitions on the disk. If the disk has partitions that were created using other tools, delete them and create new ones using Windows 7. This is how you can ensure correct partition alignment.
Install the most recent driver for the disk controller. If your computer has an Intel SATA controller, use the most latest version Intel Rapid Storage Technology driver, which can be found on the manufacturer's official website.
6. SSD Mini Tweaker
You can mark all the items with checkmarks, or rather not possible but necessary. I marked all the points, except that you can leave only SuperFetch, disabling this service can increase the startup time of programs. Check the boxes required services, and click the "Apply Changes" button. Almost everything, in the same utility there is an item "Manual", which means that you need to manually disable services. There are two of them, defragmentation of the disk on a schedule and indexing the contents of files on the disk.

7.1 Disable indexing of file content on disk
Go to "My Computer" and right-click on one of the local drives. We select "Properties".
A window will open in which you need to uncheck the box "Allow indexing the contents of files on this disk in addition to file properties". Click "Apply".

7.2 Moving index files
Windows has a great search, but good things come at a price, as they say. Absolutely all files that are in user folders and emails are indexed so that you can subsequently search the content or files. This information is located system disk as a group of files that are combined into hidden folder... Depending on how many files were indexed, the size of the index can even be several gigabytes.
Many people advise turning off this service search, but I think this is not good advice. It is much better if you move the index files to the data drive. You can do it this way:
a. Create a new empty folder for index files on the data drive. For example, I have “Index” on the “D:” drive.
b. In the search bar on the Start menu, enter the word “index” (it must be written without quotes), and then select “Indexing Options”.
d. The Index Location section contains information about the current location of the index files - by default, this is C: \\ ProgramData \\ Microsoft. You should click "Select new", and then select the folder that was created in step 1, then click "OK".

8. Moving personal folders with user data
You can save as much space as possible by moving folders named Downloads, Music, Documents, Pictures, and Videos. To do this, you need:
a. Open with Explorer the disk where you plan to move the files and create empty folders for each directory that you plan to move. You don't need to do this, but then the process will become somewhat more complicated. IN this example the data disc was named "D:".
b. Open your own profile directory using "Explorer", click with right button mouse on the folder you are going to move, and then select "Properties".
in. Open the tab called "Layout" and click the "Move" button. Now you just have to select the folder that you created in step 1 with the same name as the folder to be moved.
d. Then you just have to click on the "Apply" button. After that, a window will appear in front of you, specifying whether you really want to move files to new folder and delete the current folder. Just click Yes.

9. Minimize space for trash bin files.
If you have two drives, you should allocate a minimum amount of space for the Recycle Bin on the system disk, but on the disk with data the allocated space should be more. How much space to allocate for these purposes depends only on your desire.

10. Disable or transfer the swap file
An SSD is best used with a lot of RAM. In this situation, you can disable the swap file, which slows down and wears out the SSD.
Name of this file by default "Pagefile.sys", it is located in the root directory of the system drive. It can be shrunk or moved to a data drive. Each of these options has both its pros and cons, and calculating the correct size of the paging file is a separate conversation and an entire article may even be written on this topic.
You can change the paging file settings by clicking on the "Options" button located in the "Performance" section on the "Advanced" tab of the "System Properties" window. You will see a dialog box "Performance settings", there you should open the "Advanced" tab (you need to do this a second time), and then click the "Change" button, which is located in the "Virtual memory" section.
Then uncheck the "Automatically select paging file size" icon, and only then the new options will become available to you.
The amount of RAM on my computer was sufficient, and therefore I decided to limit the size of the paging file to 1024 MB, allowing it to expand when the need arises to 4 GB. After the settings are changed, do not forget to click on the "Set" button.
To move the paging file to another disk, select the "Without paging file" option and click on the "Set" button. Then you should select the required disk in the list and indicate its size, or choose the option "Size as selected by the system". Next, you should click "Set". 
11. Disable sleep mode (Hibernate Hibernation).
If the computer has a small disk space, hibernation can be disabled from the command line with administrator rights. To do this, in the search bar of the Start menu, enter the keyword "cmd" (you must enter it without quotes), and then press ++. A command line window will appear in front of you, there you should enter the command
powercfg -h off
and then press. You can enable hibernation using the same command line, the main thing is to put on instead of off. The command line can also help you check the size of the swap and hibernation files by simply typing dir c: \\ / as.
12. System recovery
Thanks to the "System Restore" function, you can, if necessary, return the old system settingsand also save previous versions important files. To do this, the system periodically creates restore points - these are a kind of snapshots of the current state of the system. This information is stored on the system disk and takes up a certain place. Of course, you can disable this function, but, in my opinion, this is not necessary. It would be much better to carry out some limitation of the space that has been allocated for their storage.
In order to do this, you need to open the System Properties dialog box and select the System Protection tab there. In the list, you need to select drive C, and then click the "Configure" button. You will see a dialog box where you can configure the use of disk space. As you can see, I have allocated only 3% of the total disk volume for these purposes, this will be enough to save several restore points, and this will be enough to return to the previous state of the system, of course, if this need arises. ...

13. Checking TRIM
Windows 7 and 8 should include TRIM for SSD, but this can be verified. To query the status or set parameters for using TRIM, you need a command line with administrator rights, as well as to disable hibernation.
Requesting the current status:
fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify
If the value is zero, then TRIM is enabled. If not, then you need to enable it:
fsutil behavior set disabledeletenotify 0
14. Setting up the file system.
To increase the performance and resource of the SSD, you can disable the recording of the time of the last access to the file.
fsutil behavior set disablelastaccess 1
15. Reconfigure browser cache to RAM or another HDD
Google Chrome and all browsers on the Chromium engine (CoolNovo, RockMelt, Rambler Nichrom, Yandex.Browser, [email protected]). May also work for Opera above version 15.
In order to change the cache storage path, you need to slightly edit the shortcut from which you start your chrome.
To do this, right-click on the shortcut and click "Properties". In the cell "Object" you need to add the following:
Disk-cache-dir \u003d "<путь>"
Instead of<путь> we write the desired address, it should look something like this:

By default, the cache is stored in the folder:
C: \\ Users \\<имя пользователя>\\ AppData \\ Local \\ Google \\ Chrom e \\ User Data \\ Default \\ Cache \\
You need to remove it manually. This method will only work when launched from the shortcut where you added this parameter.
16. Moving the directory for temporary files to a regular (HDD) disk
The paths to the TEMP directories are located here:
Computer - Properties - Advanced system settings - Advanced tab - Environment Variables - TMP and TEMP (for current user and general).
Someone advises transferring Temp to RAMDisk, but this is rather harmful advice. This is due to the fact that some programs (including updates) write data to a temporary directory, then send the computer to reboot, and then expect that the data has not gone anywhere during this time. And RAMDisk is cleared by default on reboot. But even if your RAMDisk supports saving data to an image and recovering after a reboot, this is not a panacea either. a situation is possible in which the RAMDisk service "but simply does not have time to start and initialize by the time the programs begin to access the temporary directory.
17. CrystalDiskMark
CrystalDiskMark - small free program, designed for comparative analysis (testing) of the performance of computer hard drives. Allows you to measure the speed of reading and writing data.
An SSD is a device that has the same purpose as a hard drive, but in terms of structure and principle of operation, it is very different from its counterpart. In particular, if the case concerned the operation of Windows installed on an SSD, you should properly optimize this deviceto significantly extend its service life.
Optimizing SSD for Windows
Suppose you have already installed Windows operating system, starting with the seventh version, on a brand new SSD. If not yet, follow the link below to learn a little instruction that will allow you to perform this procedure correctly.
The main feature of an SSD is that it has a limited number of rewriting cycles. This means that as little data as possible on the disc should be erased and re-written. First of all, it is this moment that we will take into account when optimizing SSD for the operating system of the Windows family.
Stage 1: checking if TRIM is active
TRIM - special functionintroduced in Windows 7, which finds unused areas and allows you to clear them for later writing. If the activity of this function is undesirable for HDD, then in the case of SSD it will extend the life of the drive.

Stage 2: turn off automatic defragmentation
The next point that can seriously affect the lifespan of a solid state drive is automatic defragmentation. The point is that defragmentation is useful tool for hard drives. It optimizes the recordings on the disk, which allows you to speed up the work with the HDD. In the case of SSDs, the less data is rewritten, the better.
As a rule, if an SSD is installed on the computer, Windows automatically disables this procedure, however, you should still check if this is so.
To do this, press the key combination Win + Rto open the "Run" window and write the following command in it, followed by the Enter key:
The screen will display the disk optimization menu, in which, by highlighting the item "Solid State Drive", in the lower area of \u200b\u200bthe window you should display the value "Off"... If you see item "On", to the right click on the button "Change parameters".

Uncheck the "Run on schedule (recommended)" box and then save the settings.

Stage 3: deactivate the paging file
The paging file is system file, which allows you to make up for the lack of RAM when it is fully loaded.
The bottom line is that the paging file takes over unused data from RAM to a hard drive (solid state drive). It becomes clear that when this file is active, information is regularly overwritten on the solid-state drive, which must be minimized.
Alternatively, you can completely deactivate the paging file, which will reduce the number of rewriting cycles on the solid-state drive, however, if several resource-intensive games or programs are running on the computer, rAM may end completely, which means that a message of the following plan will be displayed on your screen:


Stage 4: turn off Windows hibernation
Hibernation is a popular computer start-up mode, in which, after shutting down, the computer completely turns off, but after turning it on, it continues from where you left off. Thus, the user does not have to restart all programs, open files, and so on.
To disable hibernation, run a command prompt as administrator (as described above), and then run the following command in it:
Powercfg -h off
From now on, hibernation will be disabled, and the file responsible for it will be removed from the system.
Stage 5: turn off file indexing
The file indexing process allows you to find files on your computer faster, but due to continuous overwriting, it negatively affects the life of the SSD.

Stage 6: Activating Record Caching
Enabling the write caching function will be a plus for both the solid-state drive and the hard drive.

Stage 7: disabling Prefetch
Prefetch is a special technology to speed up system boot, which aims to work with slow media. As you can imagine, for SSD this function useless.
- Start the "Run" window with the Win + R keys and run the command in it:
HKLM SYSTEM CurrentControlSet Control Session Manager Memory Management PrefetchParameters
Double click on the parameter "EnablePrefetcher" and put the value in it «0» ... Save your changes.
These tips will help you reduce the number of SSD rewriting cycles without affecting system performance. But even if you do not resort to the tips listed in the article, the solid state drive will still for a long time please you with our excellent work. If you know what other SSD optimization techniques exist, share them in the comments.
